[Mimir 實戰] 打造本地監控系統
這篇文章中的目標是在本地端使用 docker-compose 打造監控系統,使用的 tech-stack 包含 :
- Node.js (Express.js) : 用於建立 api server
- PostgreSQL : 用於儲存資料
- Postgres Exporter : 用於輸出 PostgreSQL 的 metrics
- Alloy : 用於將不同的指標轉送到 mimir 中儲存
- Mimir : 用於儲存 metrics
- Grafana : 用於視覺化儀表板
- Curl : 用於模擬 request
Demo 的檔案結構如下 :
├─ config
│ ├─ alloy
│ │ └─ config.alloy
│ ├─ grafana
│ │ ├─ dashboards
│ │ │ ├─ nodejs.json
│ │ │ └─ postgres.json
│ │ └─ provisioning
│ │ ├─ dashboards
│ │ │ └─ dashboard.yaml
│ │ └─ datasources
│ │ └─ datasources.yaml
│ ├─ mimir
│ │ └─ mimir.yaml
│ └─ postgres
│ └─ init.sql
├─ docker-compose.yaml
├─ Dockerfile
├─ docs
│ ├─ image-1.png
│ └─ image.png
├─ index.mjs
├─ package-lock.json
├─ package.json
└─ README.md
API Setup
首先需要建立一些簡單的 api,這裡我使用 Express.js 這個框架,並用 prom-client 來記錄指標。
npm i express prom-client pg
接著在 index.js 中建立一些簡單的 api,並加上一個 middleware 來記錄指標,總共有四種不同的指標,傳送的 request 數量、request 的時間、request 的大小、response 的大小。
import express from 'express';
import promClient from 'prom-client';
import pg from 'pg';
const app = express();
app.use(express.json());
const pool = new pg.Pool({
host: 'postgres',
port: 5432,
user: 'postgres',
password: 'postgres',
database: 'postgres'
});
const register = new promClient.Registry();
register.setContentType(promClient.Registry.OPENMETRICS_CONTENT_TYPE);
promClient.collectDefaultMetrics({ register });
const httpRequestCounter = new promClient.Counter({
name: 'http_requests_total',
help: 'Total number of HTTP requests',
labelNames: ['method', 'route', 'status']
});
register.registerMetric(httpRequestCounter);
const httpRequestDurationHistogram = new promClient.Histogram({
name: 'http_request_duration_seconds',
help: 'Duration of HTTP requests in seconds',
labelNames: ['method', 'route', 'status'],
buckets: [0.01, 0.02, 0.03, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10]
});
register.registerMetric(httpRequestDurationHistogram);
const httpRequestLengthHistogram = new promClient.Histogram({
name: 'http_request_length_bytes',
help: 'Length of HTTP requests in bytes',
labelNames: ['method', 'route'],
buckets: [100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900, 1000]
});
register.registerMetric(httpRequestLengthHistogram);
const httpResponseLengthHistogram = new promClient.Histogram({
name: 'http_response_length_bytes',
help: 'Length of HTTP responses in bytes',
labelNames: ['method', 'route'],
buckets: [100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900, 1000]
});
register.registerMetric(httpResponseLengthHistogram);
app.use((req, res, next) => {
const start = Date.now();
res.on('finish', () => {
httpRequestCounter.labels(req.method, req.route.path, res.statusCode).inc();
httpRequestDurationHistogram
.labels(req.method, req.route.path, res.statusCode)
.observe(Date.now() - start);
httpRequestLengthHistogram.labels(req.method, req.route.path).observe(req.socket.bytesRead);
httpResponseLengthHistogram.labels(req.method, req.route.path).observe(req.socket.bytesWritten);
});
next();
});
app.get('/metrics', async (req, res) => {
res.set('Content-Type', register.contentType);
res.end(await register.metrics());
});
app.get('/api/book/:bookId', async (req, res) => {
try {
const result = await pool.query('SELECT id, title FROM books WHERE id = $1', [
req.params.bookId
]);
if (result.rowCount === 0) {
return res.status(404).send('Book not found');
}
res.status(200).send(result.rows[0]);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
res.status(500).send('Internal server error');
}
});
app.post('/api/book', async (req, res) => {
try {
const { title } = req.body;
if (!title) {
return res.status(400).send('Title is required');
}
await pool.query('INSERT INTO books (title) VALUES ($1)', [title]);
res.status(201).send();
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
res.status(500).send('Internal server error');
}
});
app.delete('/api/book/:bookId', async (req, res) => {
try {
await pool.query('DELETE FROM books WHERE id = $1', [req.params.bookId]);
res.status(204).send();
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
res.status(500).send('Internal server error');
}
});
app.listen(8000, async () => {
try {
await pool.connect();
await pool.query(`
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS books (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
title TEXT NOT NULL
)
`);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
process.exit(1);
}
console.log('Server is running on http://localhost:8000');
});
並使用簡單的 Dockerfile 來打包我們的 server。
FROM node:20-alpine3.18
WORKDIR /app
COPY package*.json ./
RUN npm ci --production
COPY . .
EXPOSE 8000
CMD ["node", "index.mjs"]
Docker Compose
接下來設定 docker-compose 以及各個服務的 config file :
docker compose up -d
name: mimir-demo
services:
alloy:
container_name: alloy
image: grafana/alloy:v1.7.1
restart: always
command: ['run', '--server.http.listen-addr=0.0.0.0:12345', '/etc/alloy/config.alloy']
healthcheck:
test:
[
'CMD',
'/bin/bash',
'-c',
"echo -e 'GET /-/ready HTTP/1.1\\nHost: localhost\\nConnection: close\\n\\n' > /dev/tcp/localhost/12345"
]
interval: 5s
timeout: 5s
retries: 10
start_period: 5s
volumes:
- ./config/alloy/config.alloy:/etc/alloy/config.alloy
ports:
- '12345:12345'
depends_on:
postgres:
condition: service_healthy
restart: true
mimir:
container_name: mimir
image: grafana/mimir:2.15.0
restart: always
command: ['-ingester.native-histograms-ingestion-enabled=true', '-config.file=/etc/mimir.yaml']
ports:
- '9009:9009'
volumes:
- './config/mimir/mimir.yaml:/etc/mimir.yaml'
grafana:
container_name: grafana
image: grafana/grafana:11.5.1
restart: always
environment:
- GF_AUTH_ANONYMOUS_ENABLED=true
- GF_AUTH_ANONYMOUS_ORG_ROLE=Admin
- GF_AUTH_DISABLE_LOGIN_FORM=true
healthcheck:
test: ['CMD', 'curl', '-f', 'http://localhost:3000/api/health']
interval: 5s
timeout: 5s
retries: 5
start_period: 5s
volumes:
- ./config/grafana/provisioning:/etc/grafana/provisioning
- ./config/grafana/dashboards:/var/lib/grafana/dashboards
ports:
- '3000:3000'
postgres:
container_name: postgres
image: postgres:16.8
restart: always
command:
[
'postgres',
'-c',
'shared_preload_libraries=pg_stat_statements',
'-c',
'pg_stat_statements.track=all'
]
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: postgres
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: postgres
POSTGRES_DB: postgres
healthcheck:
test: ['CMD', 'pg_isready', '-U', 'postgres']
interval: 5s
timeout: 5s
retries: 10
start_period: 5s
volumes:
- ./config/postgres/init.sql:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/init.sql
ports:
- '5432:5432'
postgres-exporter:
container_name: postgres-exporter
image: prometheuscommunity/postgres-exporter:v0.17.1
restart: always
environment:
DATA_SOURCE_NAME: 'postgresql://postgres:postgres@postgres:5432/postgres?sslmode=disable'
healthcheck:
test: ['CMD', 'pg_isready', '-U', 'postgres']
interval: 5s
timeout: 5s
retries: 10
start_period: 5s
ports:
- '9187:9187'
server:
container_name: server
build:
dockerfile: Dockerfile
restart: always
ports:
- '8000:8000'
depends_on:
alloy:
condition: service_healthy
restart: true
postgres:
condition: service_healthy
restart: true
request:
container_name: request
image: curlimages/curl:8.12.1
restart: always
command: |
sh -c 'while true; do
method=$$(echo "GET POST PUT DELETE" | tr " " "\n" | shuf -n1)
bookId=$$(shuf -i 1-100 -n1)
case $$method in
GET)
ep=$$(echo "/api/book/$$bookId" | tr " " "\n" | shuf -n1)
curl -s -X GET http://server:8000$$ep
;;
POST)
curl -s -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://server:8000/api/book -d "{\"title\": \"Book $$bookId\"}"
;;
DELETE)
curl -s -X DELETE http://server:8000/api/book/$$bookId
;;
esac
sleep 0.05
done'
Alloy
可以在 localhost:12345 中查看 alloy 的流程圖 :
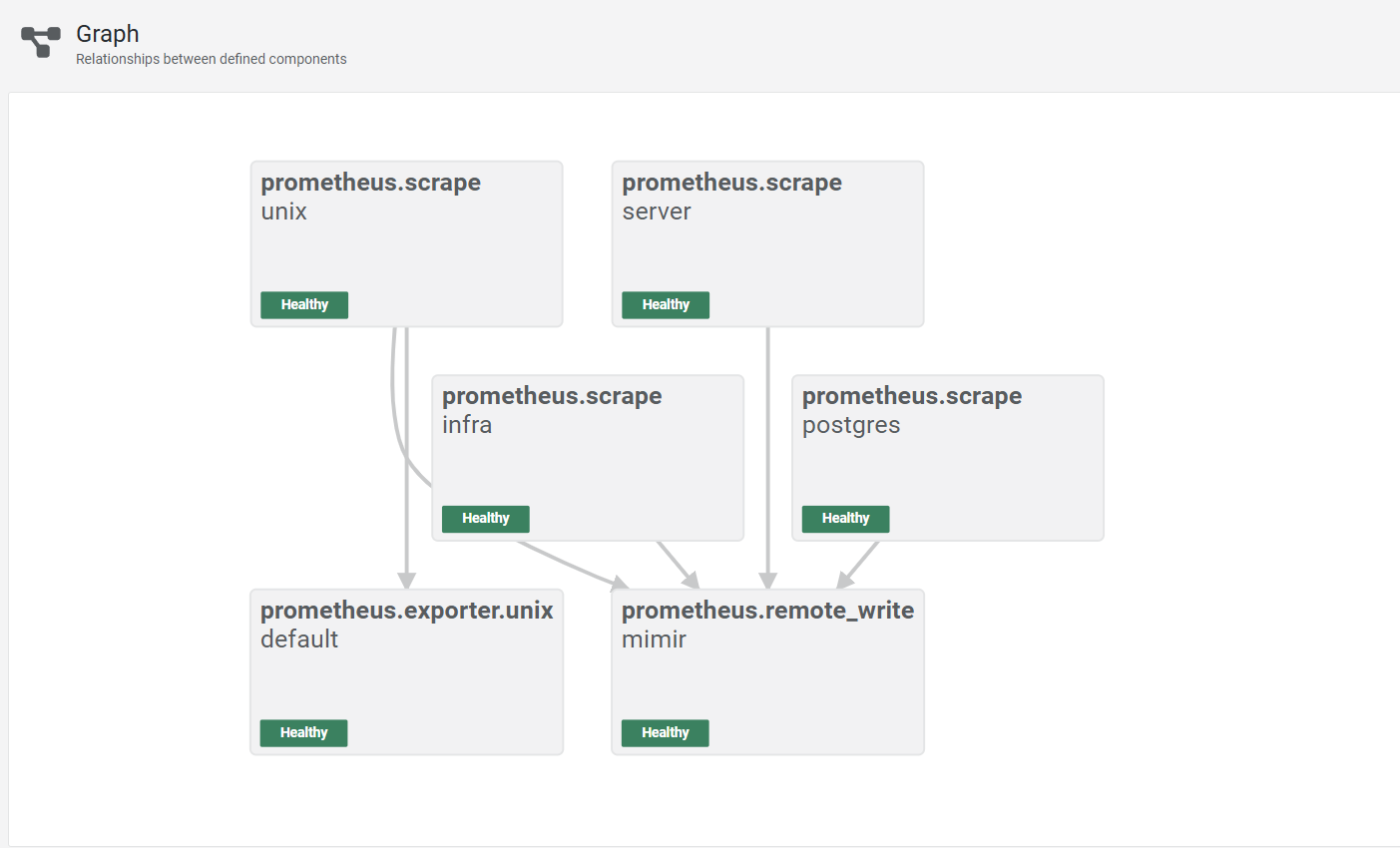
config file 的設定包含了 infra (例如 grafana、mimir、alloy 本身) 的 metrics (prometheus.scrape "infra")、
app 的 metrics (prometheus.scrape) 以及本機 (prometheus.exporter.unix ) 和 postgres 的 metrics (prometheus.scrape "postgres")。
需要注意的是,我原本打算使用 prometheus.exporter.postgres 來輸出 postgres 的 metrics,但是它似乎無法蒐集到跟 cpu 以及 memory 相關的資料,因此後來改成搭配 postgres-exporter 來輸出,如果有需要可以參考註解中的設定。
prometheus.scrape "infra" {
targets = [
{"__address__" = "mimir:9009", service = "mimir"},
{"__address__" = "grafana:3000", service = "grafana"},
{"__address__" = "localhost:12345", service = "alloy"},
]
scrape_interval = "15s"
forward_to = [prometheus.remote_write.mimir.receiver]
job_name = "infra"
}
prometheus.scrape "server" {
targets = [
{"__address__" = "server:8000", service = "server"},
]
scrape_interval = "2s"
scrape_timeout = "2s"
forward_to = [prometheus.remote_write.mimir.receiver]
job_name = "server"
}
prometheus.exporter.unix "default" {
}
// This component scrapes the Unix exporter metrics generated above.
prometheus.scrape "unix" {
targets = prometheus.exporter.unix.default.targets
forward_to = [prometheus.remote_write.mimir.receiver]
job_name = "node_exporter"
}
// // This component scrapes the Postgres exporter metrics.
// prometheus.exporter.postgres "default" {
// data_source_names = ["postgres://postgres:postgres@postgres:5432/postgres?sslmode=disable"]
// enabled_collectors = [
// "database",
// "database_wraparound",
// "locks",
// "long_running_transactions",
// "postmaster",
// "process_idle",
// "replication",
// "replication_slot",
// "stat_activity_autovacuum",
// "stat_bgwriter",
// "stat_database",
// "stat_statements",
// "stat_user_tables",
// "stat_wal_receiver",
// "statio_user_indexes",
// "statio_user_tables",
// "wal",
// ]
// }
// prometheus.scrape "postgres" {
// targets = prometheus.exporter.postgres.default.targets
// forward_to = [prometheus.remote_write.mimir.receiver]
// job_name = "postgres"
// }
prometheus.scrape "postgres" {
targets = [
{"__address__" = "postgres-exporter:9187", service = "postgres"},
]
forward_to = [prometheus.remote_write.mimir.receiver]
job_name = "postgres"
}
prometheus.remote_write "mimir" {
endpoint {
url = "http://mimir:9009/api/v1/push"
basic_auth {
username = ""
password = ""
}
}
}
Mimir
Mimir 的設定基本上也是本地的設定,並且使用 local filesystem 來儲存資料,實際上在 production 中應該要使用其他的儲存方式。
# For more information on this configuration, see the complete reference guide at
# https://grafana.com/docs/mimir/latest/references/configuration-parameters/
# Disable multi-tenancy and restrict to single tenant.
multitenancy_enabled: false
# The block storage configuration determines where the metrics TSDB data is stored.
blocks_storage:
# Use the local filesystem for block storage.
# Note: It is highly recommended not to use local filesystem for production data.
backend: filesystem
# Directory in which to store synchronised TSDB index headers.
bucket_store:
sync_dir: /tmp/mimir/tsdb-sync
# Directory in which to store configuration for object storage.
filesystem:
dir: /tmp/mimir/data/tsdb
# Direction in which to store TSDB WAL data.
tsdb:
dir: /tmp/mimir/tsdb
# The compactor block configures the compactor responsible for compacting TSDB blocks.
compactor:
# Directory to temporarily store blocks underdoing compaction.
data_dir: /tmp/mimir/compactor
# The sharding ring type used to share the hashed ring for the compactor.
sharding_ring:
# Use memberlist backend store (the default).
kvstore:
store: memberlist
# The distributor receives incoming metrics data for the system.
distributor:
# The ring to share hash ring data across instances.
ring:
# The address advertised in the ring. Localhost.
instance_addr: 127.0.0.1
# Use memberlist backend store (the default).
kvstore:
store: memberlist
# The ingester receives data from the distributor and processes it into indices and blocks.
ingester:
# The ring to share hash ring data across instances.
ring:
# The address advertised in the ring. Localhost.
instance_addr: 127.0.0.1
# Use memberlist backend store (the default).
kvstore:
store: memberlist
# Only run one instance of the ingesters.
# Note: It is highly recommended to run more than one ingester in production, the default is an RF of 3.
replication_factor: 1
# The ruler storage block configures ruler storage settings.
ruler_storage:
# Use the local filesystem for block storage.
# Note: It is highly recommended not to use local filesystem for production data.
backend: filesystem
filesystem:
# The directory in which to store rules.
dir: /tmp/mimir/rules
# The server block configures the Mimir server.
server:
# Listen on port 9009 for all incoming requests.
http_listen_port: 9009
# Log messages at info level.
log_level: info
# The store gateway block configures gateway storage.
store_gateway:
# Configuration for the hash ring.
sharding_ring:
# Only run a single instance. In production setups, the replication factor must
# be set on the querier and ruler as well.
replication_factor: 1
# Global limits configuration.
limits:
# A maximum of 100000 exemplars in memory at any one time.
# This setting enables exemplar processing and storage.
max_global_exemplars_per_user: 100000
ingestion_rate: 30000
Grafana
可以在 docker-compose 中設定好 provisioning,並且將 dashboard 與 datasource 的設定檔放在對應的資料夾中 :
apiVersion: 1
datasources:
- name: Mimir
type: prometheus
access: proxy
uid: mimir
url: http://mimir:9009/prometheus
dashboard 則可以直接參考上面的 GitHub Repo 中的 json 檔案,我使用的是以下兩個 template :
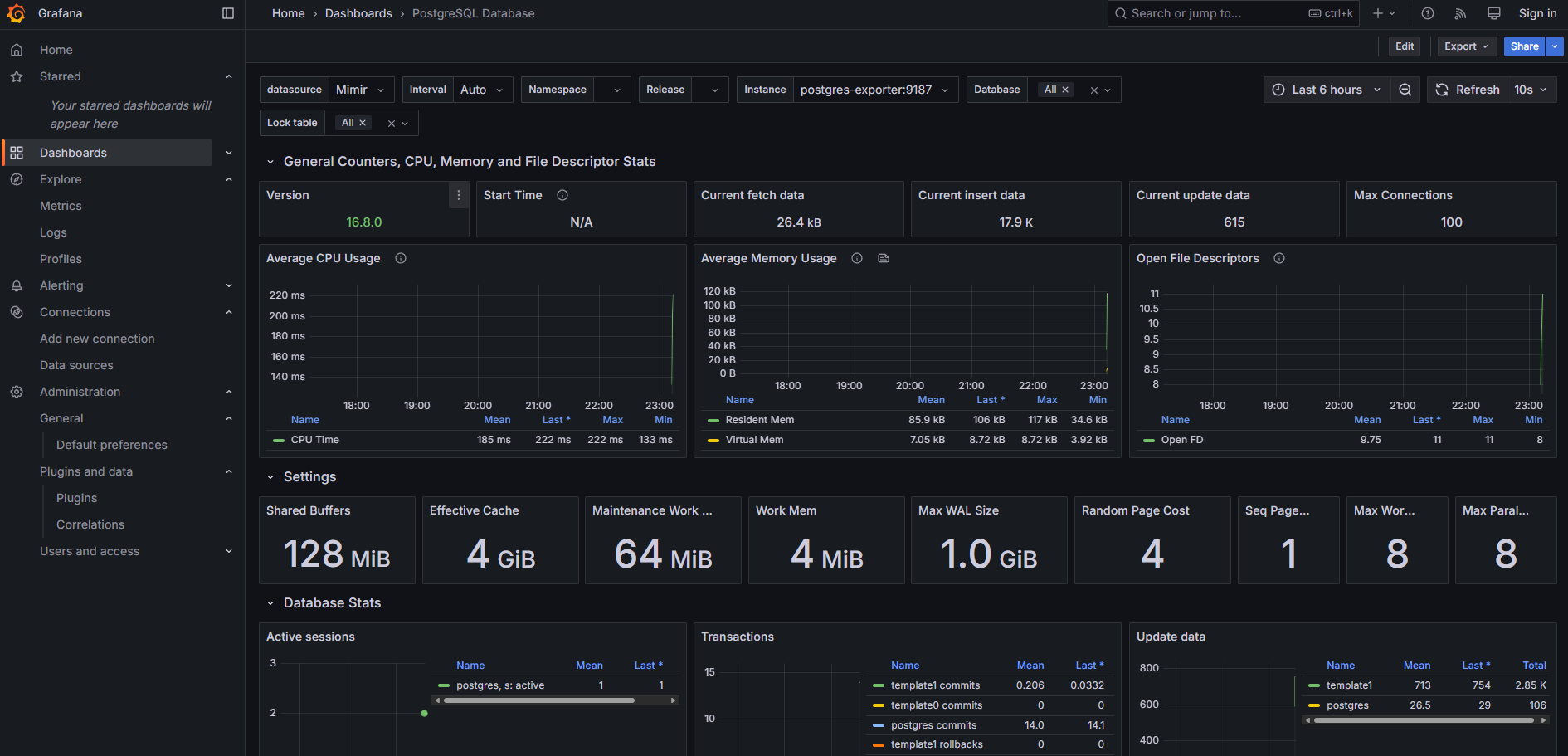
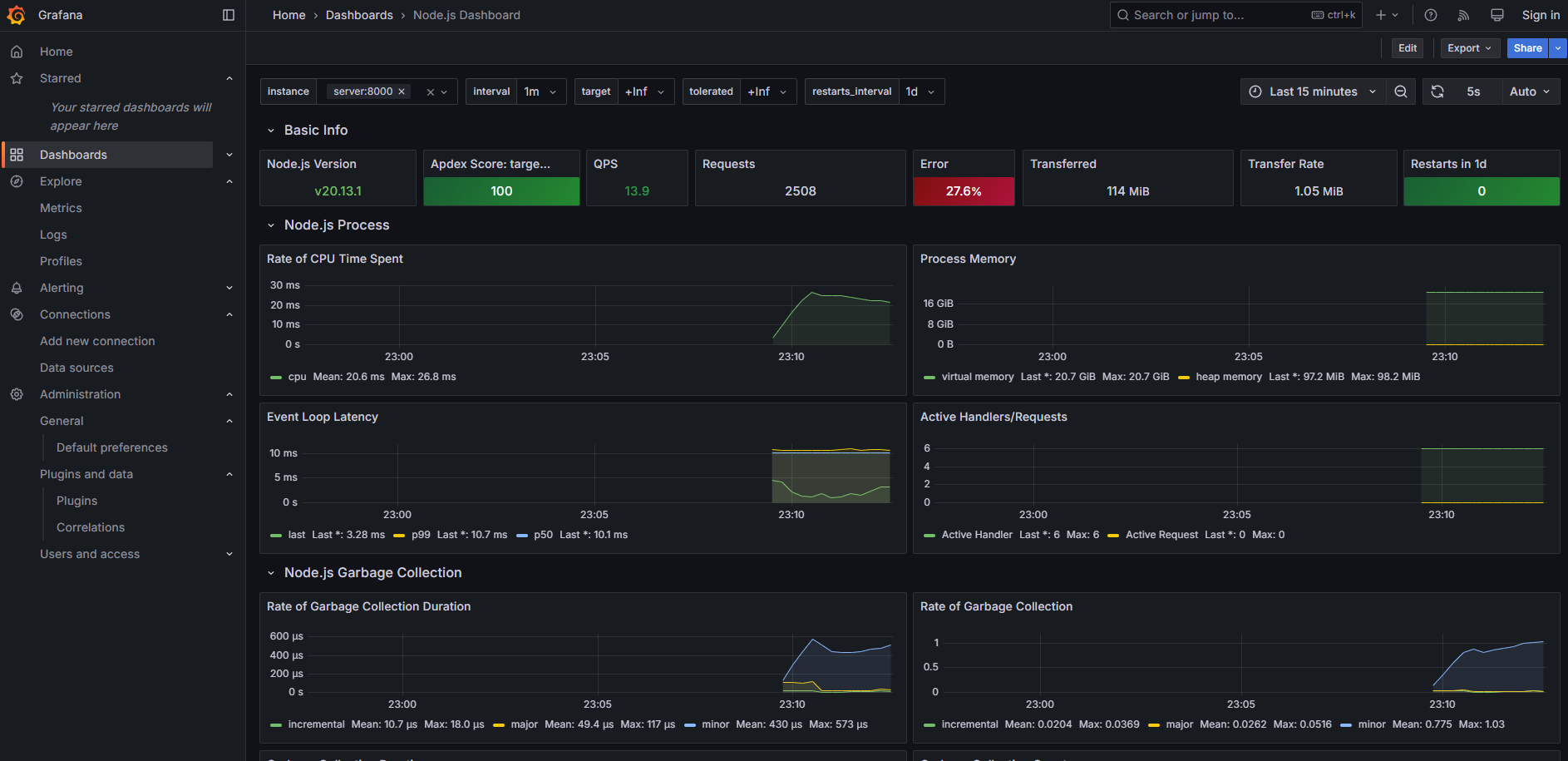
PostgreSQL
在 postgres 中我們需要啟用 pg_stat_statements 這個 extension 來記錄 query 的 performance,需要修改 config 並使用 init.sql 來初始化。
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS pg_stat_statements;
Server
剛剛建立的 api server,會開啟一個 /metrics 的 endpoint 來輸出 metrics,可以在 localhost:8000/metrics 中查看。
Request
使用 curl 指令隨機對 server 的其中一個 api 發送 request。