[Go] gRPC
這篇文章會包含一些 GRPC 的介紹,使用 Golang 作為範例
RPC
RPC (Remote Procedure Call) 是一種通訊協定,設計的目的是讓開發者無需考慮底層網絡通訊的細節,只需像呼叫本地函式一樣調用遠端方法
其中序列化的過程可以使用不同的方式,例如 JSON、XML、Protobuf 等,基於的協議也可能有所不同,常見的有 HTTP、TCP、UDP 等
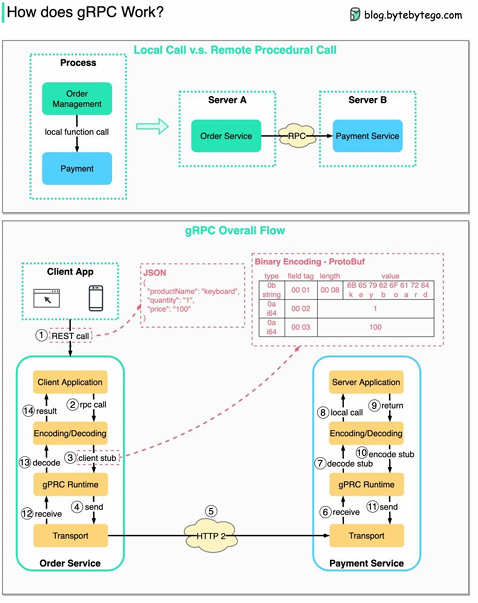
gRPC
gPRC 是一種高效的 RPC 框架,由 Google 在 2016 年開源
它基於 HTTP/2 協議,使用 Protobuf 作為序列化工具
HTTP/2 的特性如下 :
- 多路複用 : 可以在一個連接上同時進行多個請求
- Header 壓縮 : 透過 HPACK 壓縮 header,減少傳輸的大小,詳情可以參考 Reference
- 二進制協議 : HTTP/2 是一個二進制協議,可以更快的解析和傳輸
Protobuf 的特性如下 :
- 可讀性 : Protobuf 的定義是一個文本檔案,可以很容易的閱讀和修改並且添加註釋
- 節省網路流量 : Protobuf 是一個二進制協議,因此比 JSON 和 XML 更小,節省了網路流量
- 節省 CPU : ParseJson 需要消耗大量的 CPU,而 Protobuf 由於更接近二進制,因此消耗更少的 CPU
gRPC 總共有四種類型的服務 :
- Unary RPC : 一個請求對應一個回應
- Server Streaming RPC : 一個請求對應多個回應
- Client Streaming RPC : 多個請求對應一個回應
- Bidirectional Streaming RPC : 多個請求對應多個回應
service StudentService {
rpc GetStudentInfo (GetStudentRequest) returns (Student);
rpc GetStudentList (GetStudentListRequest) returns (stream Student);
rpc GetStudentInfoList (stream GetStudentRequest) returns (Student);
rpc GetStudentInfoList (stream GetStudentRequest) returns (stream Student);
}
雖然 gRPC 有很多優點,但是也有一些缺點,例如目前主流的瀏覽器還不支援 HTTP/2,因此如果要在瀏覽器中使用 gRPC,可能需要透過 grpc-web 來實現,這也導致了現在 gRPC 主要使用在後端服務之間的通訊
gRPC Example
在實作階段,我們會從頭到尾時做一個簡單的 grpc 通訊,包含一個簡單的 service,並且透過 grpc 來呼叫
Environment Setup
進入專案目錄,並且 init 一個 go module
go mod init grpc
安裝 protobuffer (windows),需要去 官網 下載對應的版本,解壓縮到專案目錄並設定環境變數
protoc --version
接著安裝 Go 的 protoc plugin
go get github.com/golang/protobuf/protoc-gen-go
go install github.com/golang/protobuf/protoc-gen-go
go get google.golang.org/grpc/cmd/protoc-gen-go-grpc
go install google.golang.org/grpc/cmd/protoc-gen-go-grpc
Protobuf
新增 /pb/student_service.proto 檔案,內容如下
syntax = "proto3";
package pb;
option go_package = "./pb;student_service";
message Student {
string name = 1;
repeated string locations = 2;
map<string, float> scores = 3;
bool gender = 4;
int32 age = 5;
float height = 6;
}
message GetStudentRequest {
string studentId = 1;
}
service StudentService {
rpc GetStudentInfo (GetStudentRequest) returns (Student);
}
syntax: 指定 proto 的版本package: 與 Go 類似,需要指定一個 package 名稱來方便將來互相 import,並且避免命名衝突option go_package: 指定生成的 Go 程式碼的 package 名稱,;左邊是代表生成的路徑,右邊是轉成 Go 的 package 名稱message: 定義一個 message,類似於 Go 的 struct,可以包含多個 fieldservice: 定義一個 service,包含多個 rpc 方法
有關於 proto 的更多語法可以參考 Reference
接著使用 protoc 來編譯 proto 檔案
protoc --go_out=. --go_opt=paths=source_relative --go-grpc_out=. --go-grpc_opt=paths=source_relative pb/student_service.proto
--go_out: 生成 Go 的 proto 檔案路徑--go_opt: 設定生成的路徑,相對於 .proto 檔案,如果不指定則會放到 package 指定的路徑下--go-grpc_out: 生成 Go 的 grpc 檔案路徑--go-grpc_opt: 設定生成的路徑,相對於 .proto 檔案,如果不指定則會放到 package 指定的路徑下pb/student_service.proto: 需要編譯的 proto 檔案
之後執行指令來更新 grpc 所需的套件
go mod tidy
執行完上面的指令之後,會在專案目錄下生成 pb/proto/student_service.pb.go 和 pb/proto/student_service_grpc.pb.go 兩個檔案
student_service.pb.go: 包含 proto 檔案生成的 structstudent_service_grpc.pb.go: 包含 proto 中的service轉換而成的 Go 程式碼
Server
產生完成程式碼之後就可以來實作 server 了,先創建一個 main.go 檔案
我們的目標是實現一個 struct 來滿足 StudentServiceServer interface
type StudentServiceServer interface {
GetStudentInfo(context.Context, *GetStudentRequest) (*Student, error)
mustEmbedUnimplementedStudentServiceServer()
}
server.go 的內容如下,我們需要滿足 StudentServiceServer interface,因此我們實作了 GetStudentInfo 方法以及繼承了 UnimplementedStudentServiceServer,這樣就滿足了 interface
package main
import (
"context"
"errors"
"fmt"
"net"
student_service "grpc/pb"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
)
type StudentServer struct {
student_service.UnimplementedStudentServiceServer
}
func (s *StudentServer) GetStudentInfo(ctx context.Context, request *student_service.GetStudentRequest) (*student_service.Student, error) {
if len(request.StudentId) == 0 {
return nil, errors.New("studentId is required")
}
student := &student_service.Student{
Name: "John Doe",
Locations: []string{"New York", "Los Angeles", "San Francisco"},
Scores: map[string]float32{
"Math": 95.5,
"English": 88.0,
"Science": 92.3,
},
Gender: true,
Age: 21,
Height: 175.5,
}
return student, nil
}
func main() {
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", "127.0.0.1:8000")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fmt.Println("Server is running on port 8000")
server := grpc.NewServer()
student_service.RegisterStudentServiceServer(server, new(StudentServer))
err = server.Serve(lis)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
接著執行 go run main.go,這樣就啟動了一個 grpc server
Client
最後我們用一個單元測試來測試 server 是否正常運作,創建一個 grpc_test.go 檔案
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"testing"
"time"
student_service "grpc/pb"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"google.golang.org/grpc/credentials/insecure"
)
func TestService(t *testing.T) {
conn, err := grpc.NewClient("127.0.0.1:8000", grpc.WithTransportCredentials(insecure.NewCredentials()))
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("connect failed %v\n", err)
t.Fail()
}
defer conn.Close()
client := student_service.NewStudentServiceClient(conn)
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), time.Second)
defer cancel()
res, err := client.GetStudentInfo(ctx, &student_service.GetStudentRequest{StudentId: "123"})
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("get student info failed %v\n", err)
t.Fail()
}
fmt.Printf("Name %s Age %d Height %.1f\n", res.Name, res.Age, res.Height)
}
最後開啟一個新的終端機執行 go test -v,如果沒有錯誤的話,就代表 server 和 client 都正常運作了