Sorting & Aggregations Algorithms
這篇筆記會探討資料庫中 Sorting 與 Aggregation 演算法的原理與實作。
Sorting
對於 relational model 來說,它不保證輸出的 tuple 有任何順序關係,但有時候我們需要對結果進行排序,常見的情況如下 :
ORDER BY- 使用
DISTINCT去除重複的 tuple 時 - 當需要大量插入資料到 B+Tree 時,如果有排序就能加快速度
- Aggregations (GROUP BY)
如果資料的大小可以放入記憶體中,我們就可以使用一般的演算法來進行排序 (quick sort / tim sort),否則我們就必須考慮到 disk I/O 的成本來選擇排序演算法。
TOP-N Heap Sort
如果我們的 SQL 指令中同時有 LIMIT N 和 ORDER BY 時,我們就可以使用 heap sort 來實現。
這種方法的好處是我們只需要掃一次所有資料並且維護一個大小為 N 的 heap 即可。

External Merge Sort
當資料量大於記憶體時,我們就需要使用外部排序 (external sort) 來處理。
外部排序通常會使用 divide and conquer 的方式來實現,主要包含 2 個步驟 :
- sorting : 將資料分割成小塊,並且在 memory 中進行排序
- merging : 將排序好的資料合併
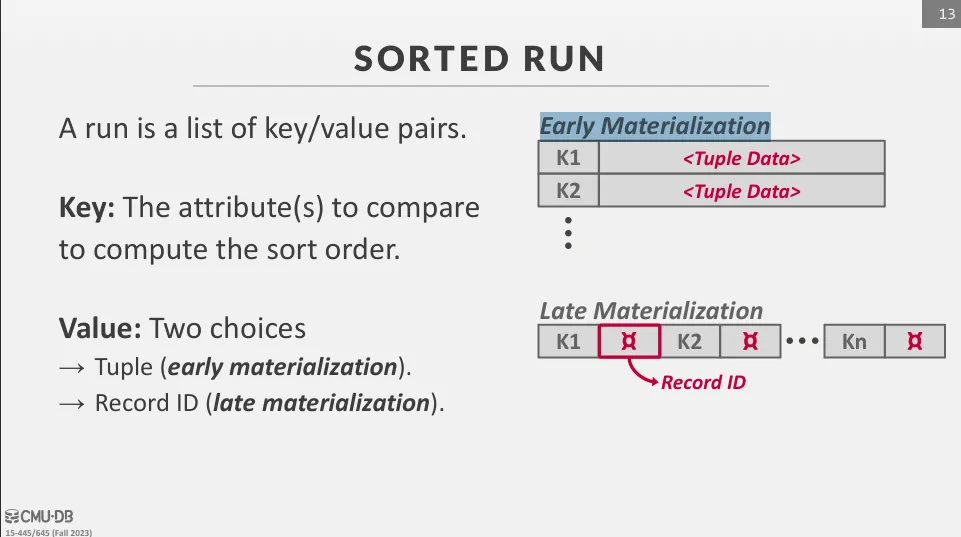
頁面內的排序可以使用 early materialization 或 late materialization 來實現 :
- early materialization : 排序頁面中會儲存完整的資料
- late materialization : 只儲存 record_id 或指標
General (K-way) Merge Sort
我們假設 file 被分成 N 個 page,且 DBMS 有 B 個 frame。
第一步 sorting 會將資料分成 個 run,每個 run 的大小為 B page,並且全部載入記憶體中進行排序,接著再將排序好的 run 寫回硬碟。
第二步 merge 就會將這些 run 進行合併,假設我們有 B 個 frame,我們會使用其中一個 frame 作為輸出 buffer,剩下的 B - 1 個 frame 用來存放每個 run 的當前 page。 我們會從每個 run 中取出最小的 tuple,並將其寫入輸出 buffer 中,當輸出 buffer 滿了之後,我們就將其寫回硬碟中,並繼續這個過程直到所有的 run 都被合併完。 在這裡,K-way merge sort 的 K 值為 B - 1。
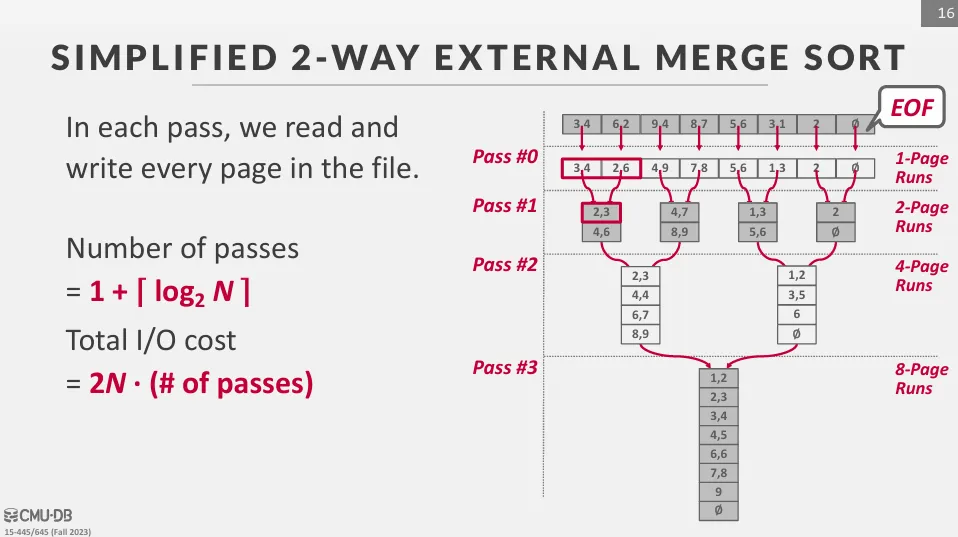
接下來讓我們來計算一下 external merge sort 的 I/O 成本,在處理大量資料時,我們常會用 pass 來表示整個資料被讀取並寫回硬碟的過程,一次 pass 包含兩個 I/O 操作 (讀取與寫回)。
在 sorting 階段,每個 page 都會被讀取並寫回一次,因此成本為一個 pass (2N)。
而在 merge 階段,每一輪都會完整的讀取所有的 page 並寫回,因此成本也是一個 pass (2N)。 我們總共需要執行 輪的 merge。
因此 external merge sort 的總 I/O 成本為 個 pass,即 。
External Merge Sort Optimizations
Double Buffering Optimization
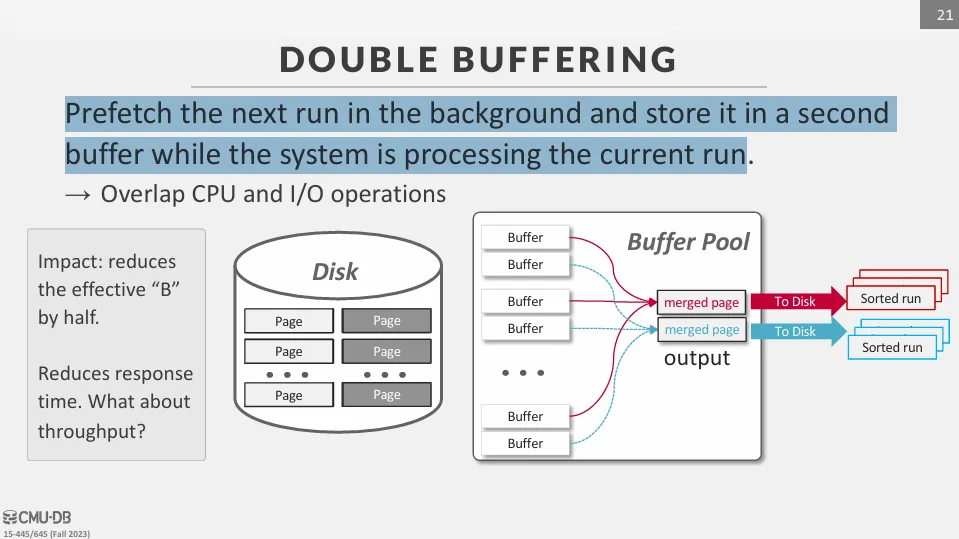
在 merge 階段,我們可以使用 double buffering 來減少等待 I/O 的時間。
當一個 buffer 正在被寫回硬碟時,另一個 buffer 可以繼續被填滿,這樣就能減少等待時間。
Comparison Optimizations
Code Specialization
通用的排序函數通常接受一個函數指標 (Function Pointer) 或 callback 作為比較器,例如 C++ std::sort 的 Compare 參數。 每次比較,CPU 都需要透過函數指標進行一次間接呼叫 (Indirect Call)。這會打斷 CPU 的指令管線 (instruction pipeline),並可能導致分支預測失敗,效能較差。 因此我們可以將函數指標內聯 (inline) 到排序函數中,這樣就能減少間接呼叫的次數,提升效能。
Suffix Truncation
如果排序的是長字串 (VARCHAR),我們可以只比較字串的前幾個字元,這樣就能減少比較的次數,提升效能。
Using B+tree
如果已經有 B+tree 的索引,我們只需要使用 B+tree 來快速遍歷 leaf node 即可得到排序好的資料,但會分成兩種情況 :
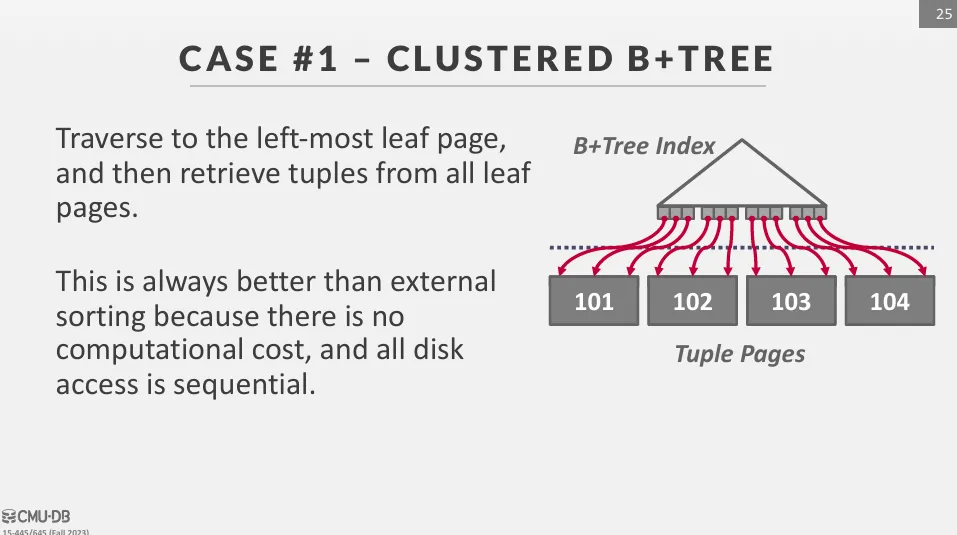
Clustered B+tree
I/O 是有順序的,比外部排序效率更高
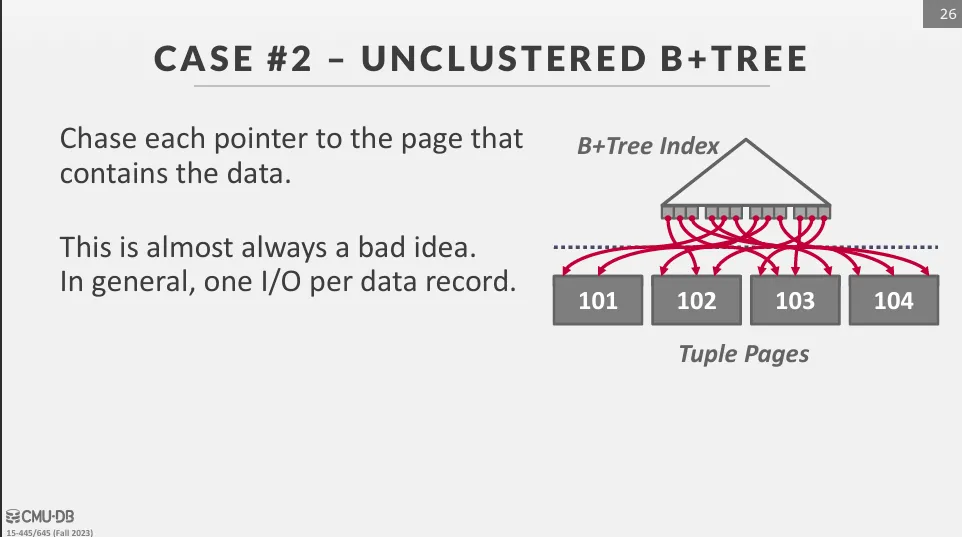
Unclustered B+tree
I/O 是隨機的,效率極低
Aggregations
為了將多個 tuple 的單個屬性合併成一個值,DBMS 需要能將資料快速分組的方法。
Sorting
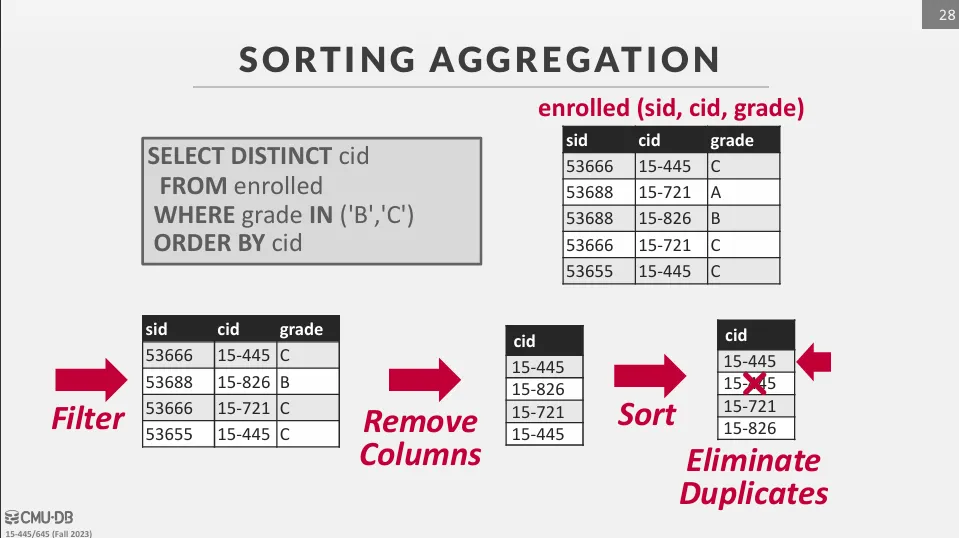
將資料依照 grouping key 排序,然後進行聚合,這種方法的好處是可以利用排序的結果來加速聚合運算,但缺點是排序的成本較高,特別是當資料量大於記憶體時。
如下圖的範例,由於我們使用了 DISTINCT,因此我們需要先將資料排序,接著再進行聚合。
Hashing
如果我們不需要最後輸出的結果是排序的,我們可以使用 hashing 來進行聚合。 這種方法的好處是可以在一次掃描中完成聚合運算,缺點是需要額外的記憶體來存放 hash table。
使用這種方式會有兩個階段 :
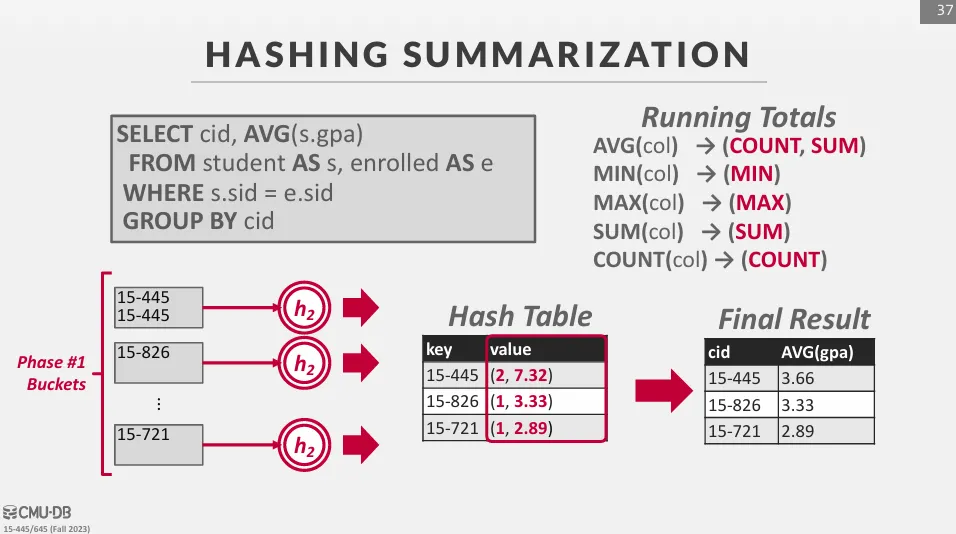
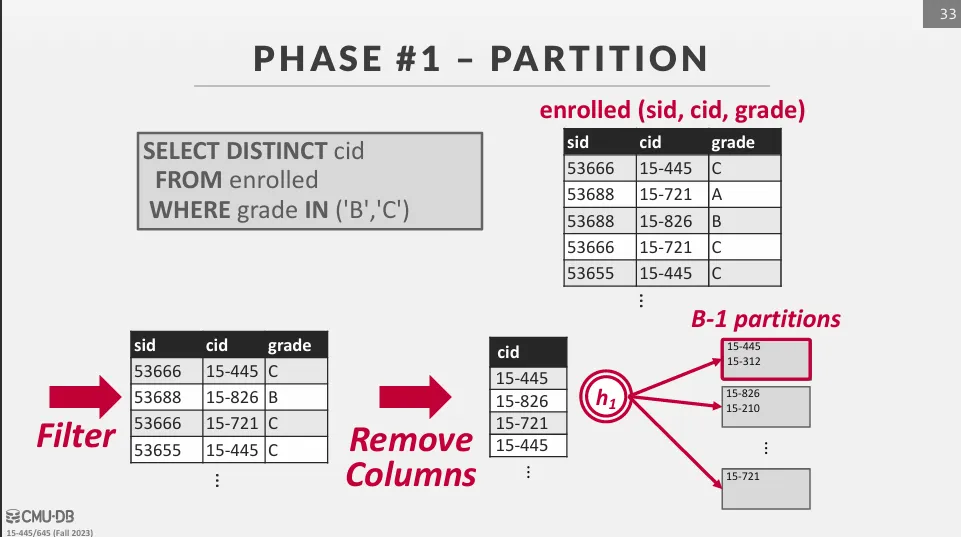
Phase 1 : Partition
先將一個巨大的資料集分割成多個較小的 partition,並保證相同的 grouping key 會被分配到同一個 partition 中。
如果我們總共有 B 個 frame 可以使用,使用 hash function h1 來將 tuple 分配到 B - 1 個 partition 中,剩下的一個 partition 用來存放輸入的資料。
Phase 2 : ReHash
把每個 partition 都逐一讀到記憶體裡,並使用 hash function h2 來建立一個新的 hash table 來進行聚合運算。 這裡不使用同一個 hash function 的原因是為了避免資料傾斜,如果 h1 已經把大量不同的鍵值分配到同一個 partition 中,我們會希望 h2 能將這些鍵值均勻地分配到 hash table 中。
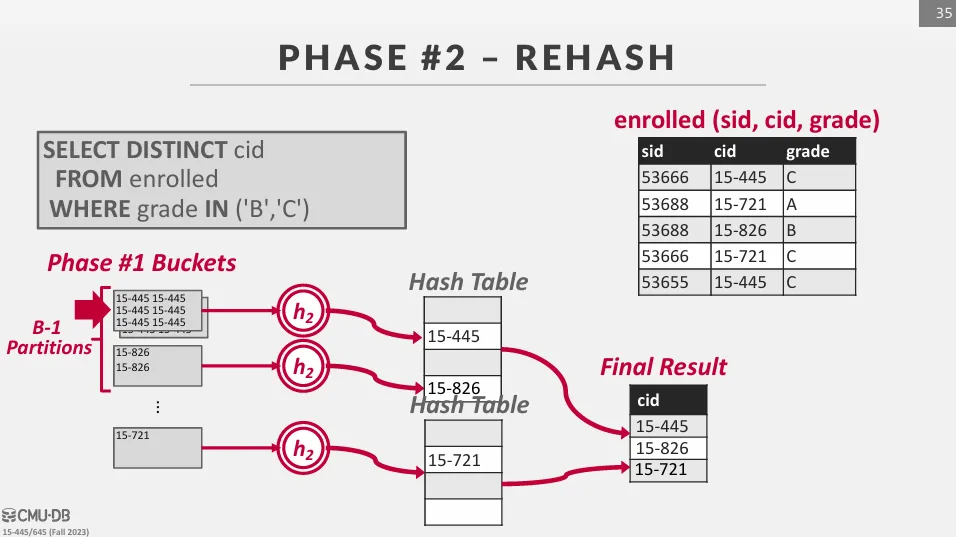
在 rehash 的過程中,存在一組 grouping key -> return value 的 hash table,我們只需要更新這個 key-value pair 即可。