Index Concurrency Control
在之前討論的資料結構中,為了討論方便,所以只考慮了 single-threaded 的情況,但在實際情況中,除了一些特別的資料庫 (如 VoltDB、Redis) 之外,大部分的 DBMS 都需要透過 multi-threaded 來利用多核心的優勢。
本節要討論的 concurrency control 就是討論在 multi-threaded 的情況下,要如何確保結果是正確的。
我們通常會從兩個層面來討論 concurrency control 的正確性 :
- Physical Correctness : 內部的資料是否正確 (本篇重點)
- Logical Correctness : 我們是否能看到應該看到的資料 (後面會討論)
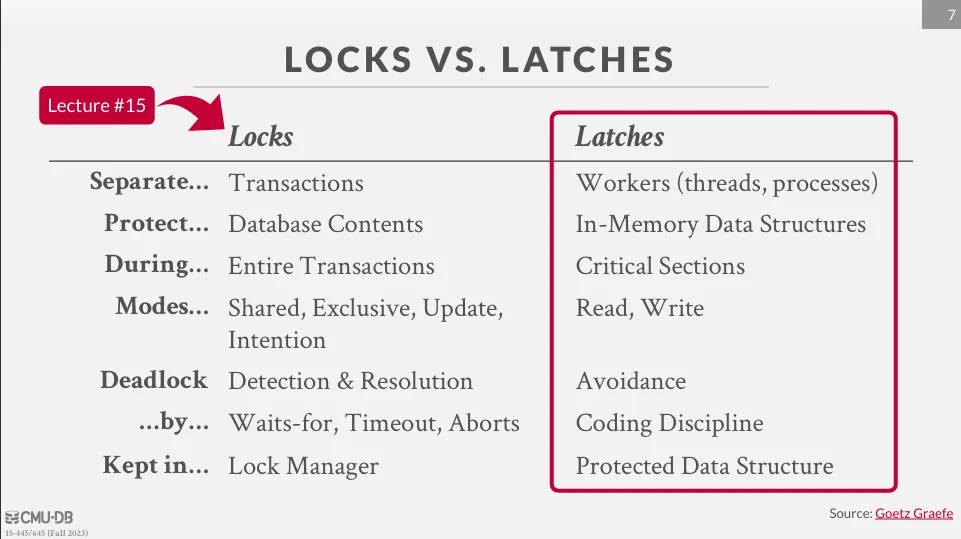
Locks & Latches
這裡我們會重點討論 latch,在 latch 中有兩種 mode :
- read mode
- 多個 thread 同時讀取
- 當別的 thread 已經有 latch 時,可以再取得 read latch
- write mode
- 只能有一個 thread 取得 write latch
- 當別的 thread 已經有任一種模式的 latch 時,就無法獲得 write latch
Latch Implementations
在實現上,latch 不應該佔據太多的記憶體,且在沒有競爭的情況下,要有快速獲取的方法。
在 DBMS 中,主要有以下幾種實現方式 :
- Test-and-Set Spin Latch (TAS)
- Blocking OS Mutex
- Reader-Writer Latches
除此之外,還有一些更為複雜的實現方式,但在這裡不做討論。
- Adaptive Spinlock (Apple ParkingLot) : 當有競爭的時候,先進行 spin 一段時間,如果還是無法獲取就放棄並且進入睡眠
- Queue-based Spinlock (MCS Locks) : 創建一個 queue 來管理等待的 thread,當有 thread 釋放鎖的時候,通知下一個 thread 獲取鎖
- Optimistic Lock Coupling (The Germans) : 專門用在樹狀結構上,樂觀的方式來獲取子節點的鎖
Test-and-Set Spin Latch (TAS)
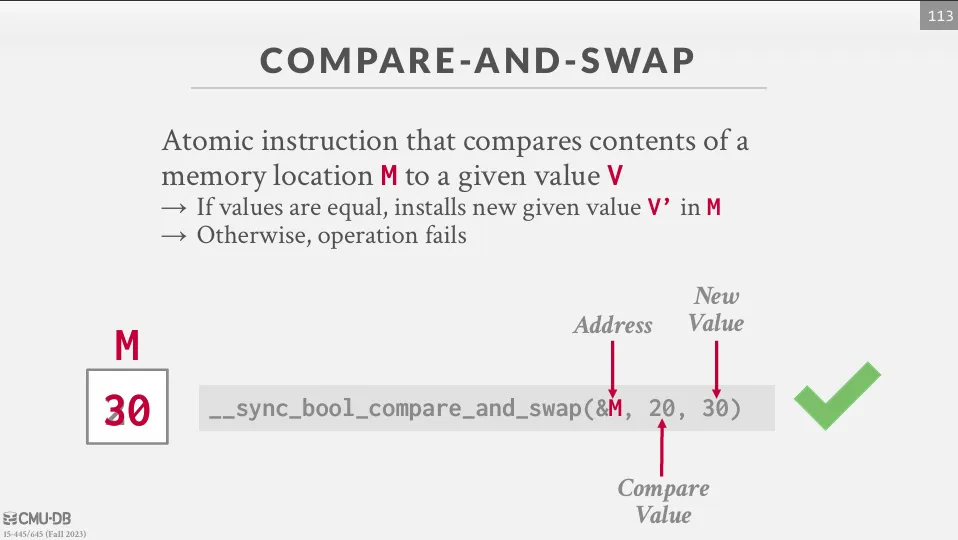
這種方式的原理是 thread 不斷的執行 CAS (Compare-And-Swap) 來更新一個記憶體中的位置,並由 DBMS 來控制成功或失敗後的行為。
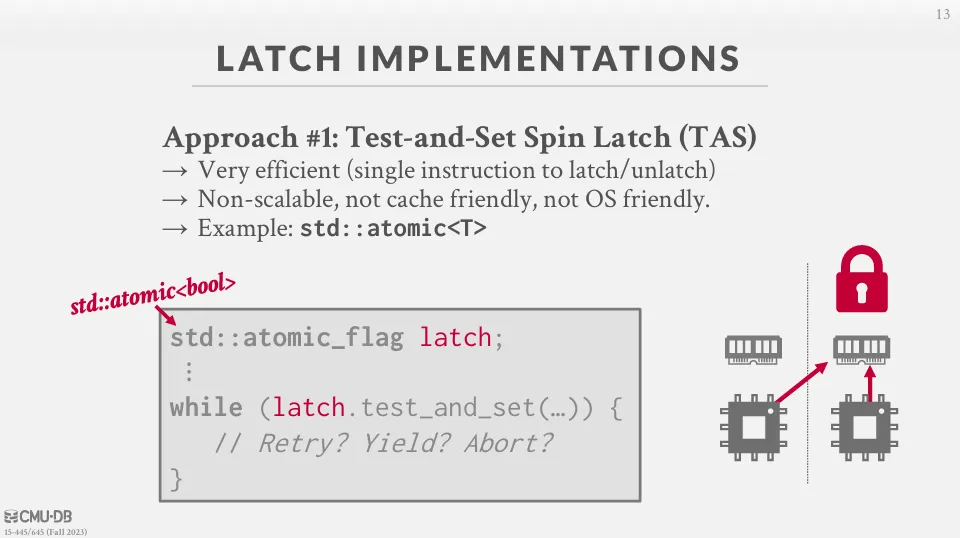
- 優點
- 效能佳
- 缺點
- 無法擴展以及 cache coherence (快取一致性) 的問題,且 CAS 指令會在多個不同的執行緒上執行,浪費 CPU bus 的資源
- 範例
std::atomic<T>
CAS 是一種原子操作,它比較一個內存位置的值與給定的預期值,如果它們相同,則將該內存位置的值更新為新值,由於是原子操作,所以不會被其他 thread 中斷。
Blocking OS Mutex
這種方式是直接使用由 OS 所提供的互斥鎖,與 spinlock 不同的是,當 thread 無法獲取鎖的時候,會進入睡眠狀態並且交出 CPU 的控制權,等到鎖被釋放的時候再被喚醒。
在 Linux 的 futex 中,DBMS 會先嘗試獲得 user-space mutex,如果獲取成功則代表 latch 被成功設定,如果失敗的話就會去嘗試獲取 kernel-space mutex,如果依然無法獲得就會被放進 block scheduler,而 block scheduler 會決定下一個要被執行的 thread。
- 優點
- 使用簡單
- 缺點
- 效能較差 (每次鎖定和解鎖需要 25ns)
- 與 spinlock 相比,context switch 的開銷較大 (因為要進入睡眠狀態)
- 範例
std::mutex
Reader-Writer Latches
這種方式是建立在 spinlock 之上,但與前面兩種方式不同,這種方式可以允許 latch 以 read mode 或 write mode 來被取得。 我們會追蹤有多少 thread 取得了 latch 以及有多少 thread 在等待 latch,並依據不同的 policy (如 reader-preferred、writer-preferred、fair reader-writer locks) 來維護 priority queue 來決定下一個要被執行的 thread。
- 優點
- 允許併發的讀取,在讀多寫少的情況下效能較佳
- 缺點
- 實作較為複雜
- 有可能會有 starvation 的問題
- 需要額外的儲存空間來儲存需要用來排序的 metadata
- 範例
std::shared_mutex
Hash Table Latching
對於 hash table 來說併發控制是相對簡單的,這是因為 hash table 一次只會訪問一個 page 或 slot,因此不會有 deadlocks 的問題。
如果 hash table 需要 resize 的時候,我們只需要對整個 hash table 加鎖即可,動態的 hash table 也是透過類似的方式實現。
主要有兩種方式來實現 hash table 的 latch (依據粒度) :
- Page Latches
- Slot Latches
Page Latches
每個 page 都有自己的 latch 來保護整個頁面的資料,thread 在訪問 page 的時候需要先獲得 read / write 的 latch。
- 優點
- 單個 thread 訪問同一 page 的多個 slot 時速度快
- 缺點
- 併發度低,因為只有一個 thread 可以訪問 page
Slot Latches
每個 slot 都有自己的 latch 來保護 slot 的資料。
- 優點
- 併發度高,因為不同的 thread 可以訪問不同的 slot
- 缺點
- 增加了 latch 的數量,可能會增加儲存和計算的 overhead
除了上述的兩種方式,也可以使用 latch-free 的方式來實現 hash table,直接使用 CAS 來探測是否可以進行操作,在某些情況下可以提高效率。
B+Tree Latching
在 B+Tree 中,我們需要考慮以下兩個情況 :
- 多個 thread 同時修改同一個 node
- 一個 node 在遍歷的時候另一個 thread 在 merge / split
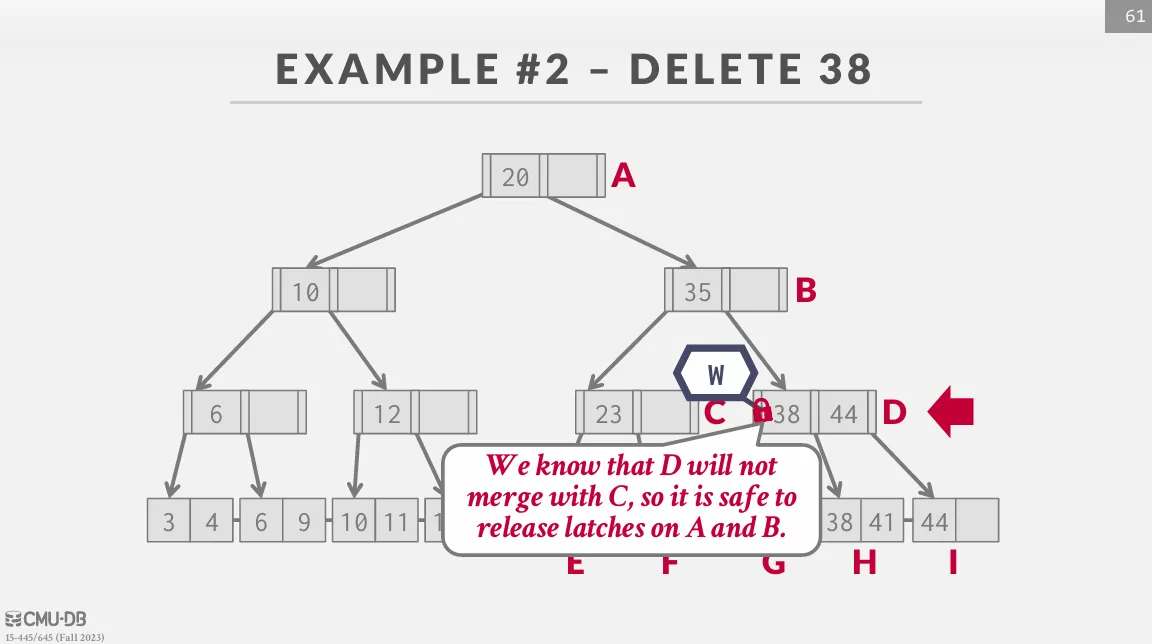
Latch Crabbing / Coupling
Latch Crabbing 是一種可以允許多個 thread 同時訪問 (修改) 一個 node 的協定,基本思路如下 :
- 獲取 parent 的 latch
- 獲取 child 的 latch
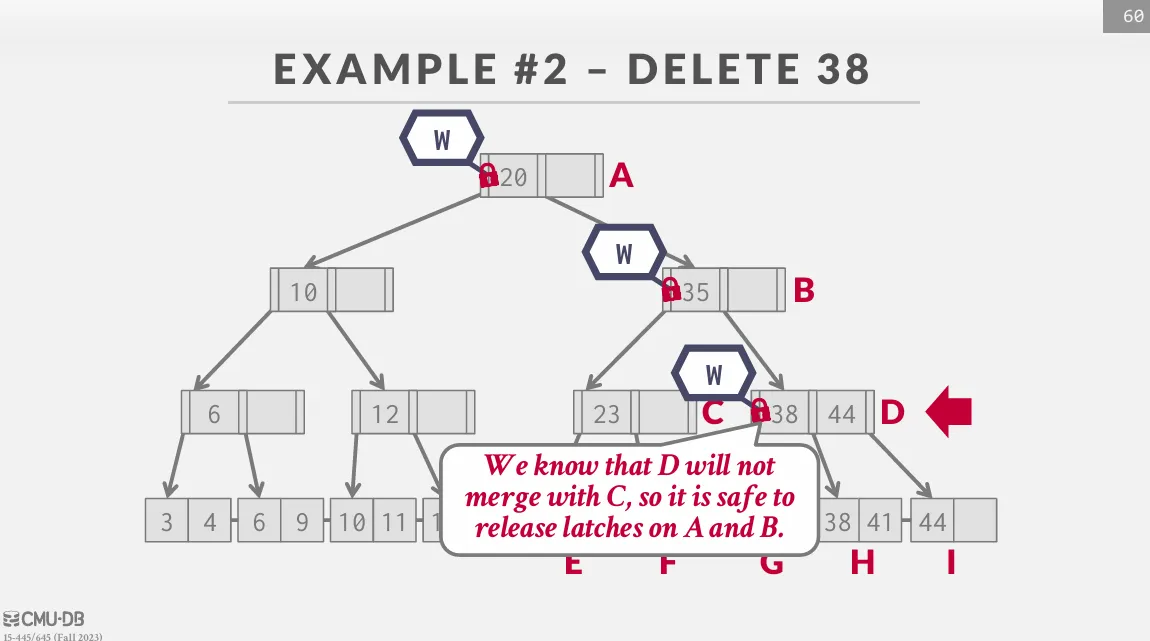
- 如果 child 是
safe的話,就釋放 parent 的 latch
safe 的定義是發生操作時,該節點不會被 merge / split :
- insert : 該節點未滿
- delete : 該節點超過半滿
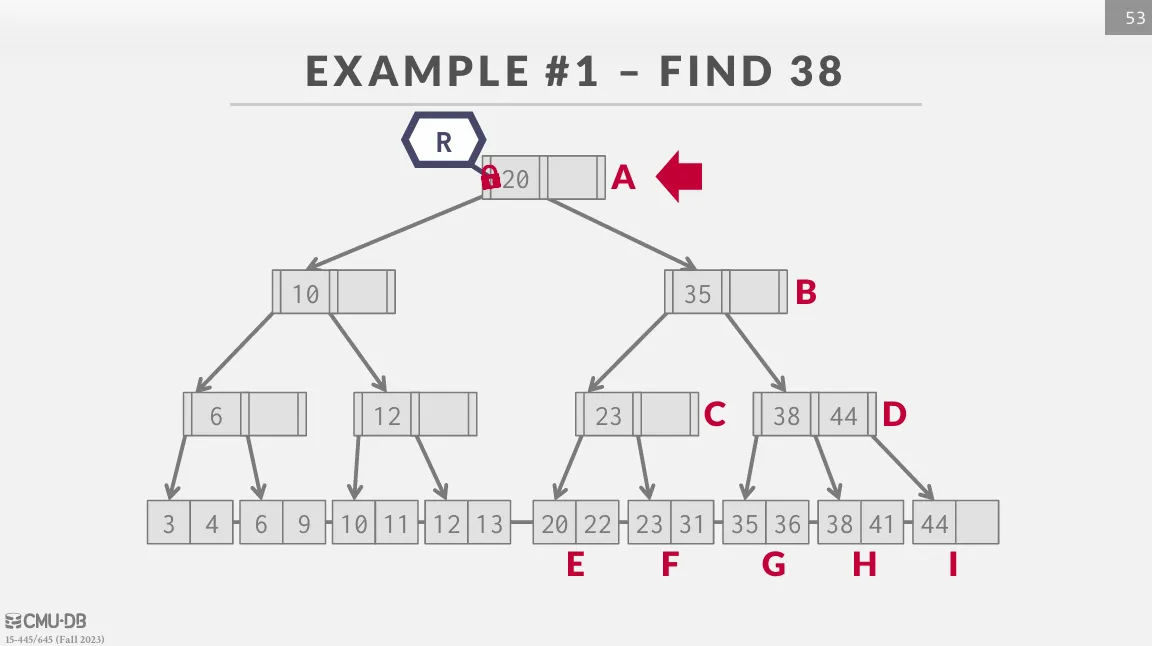
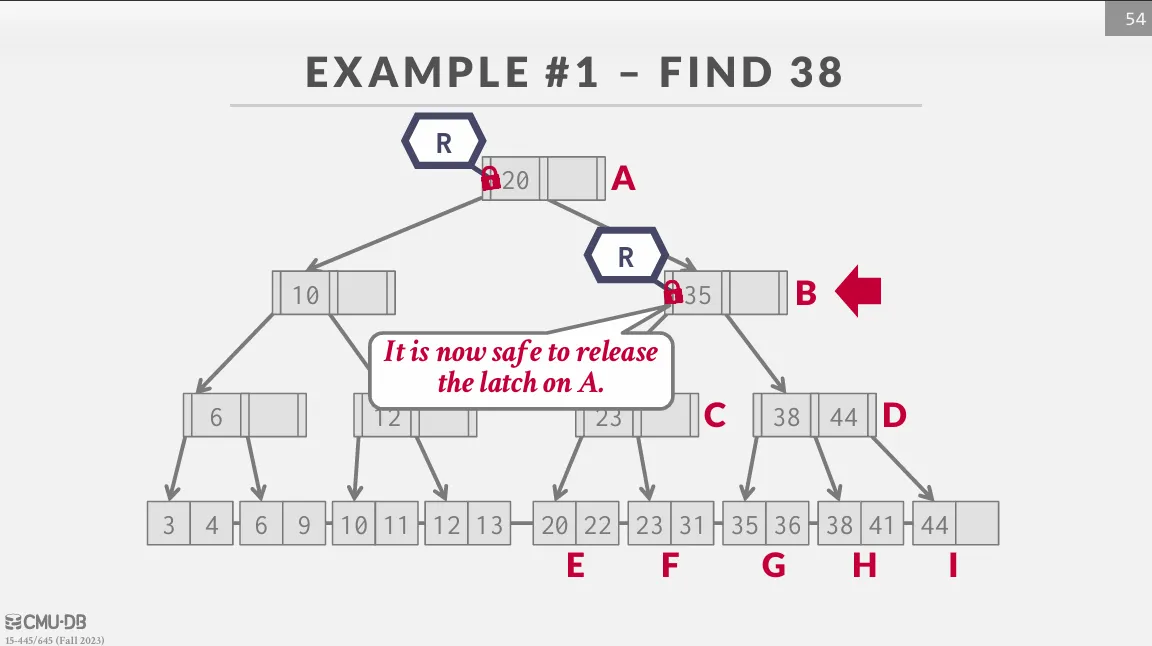
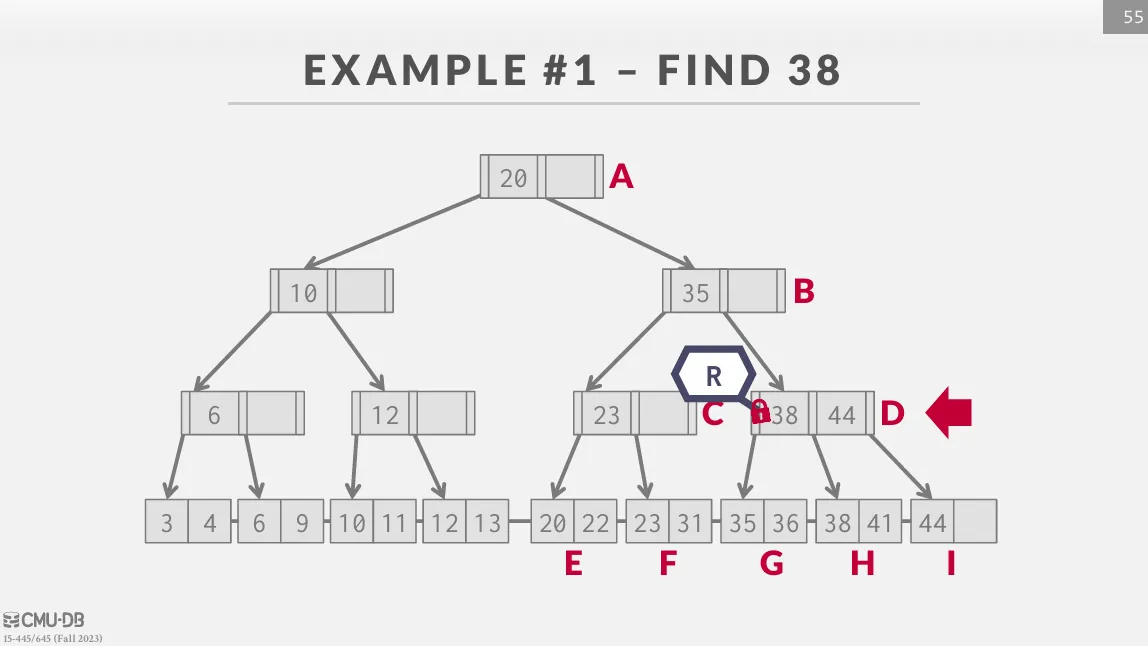
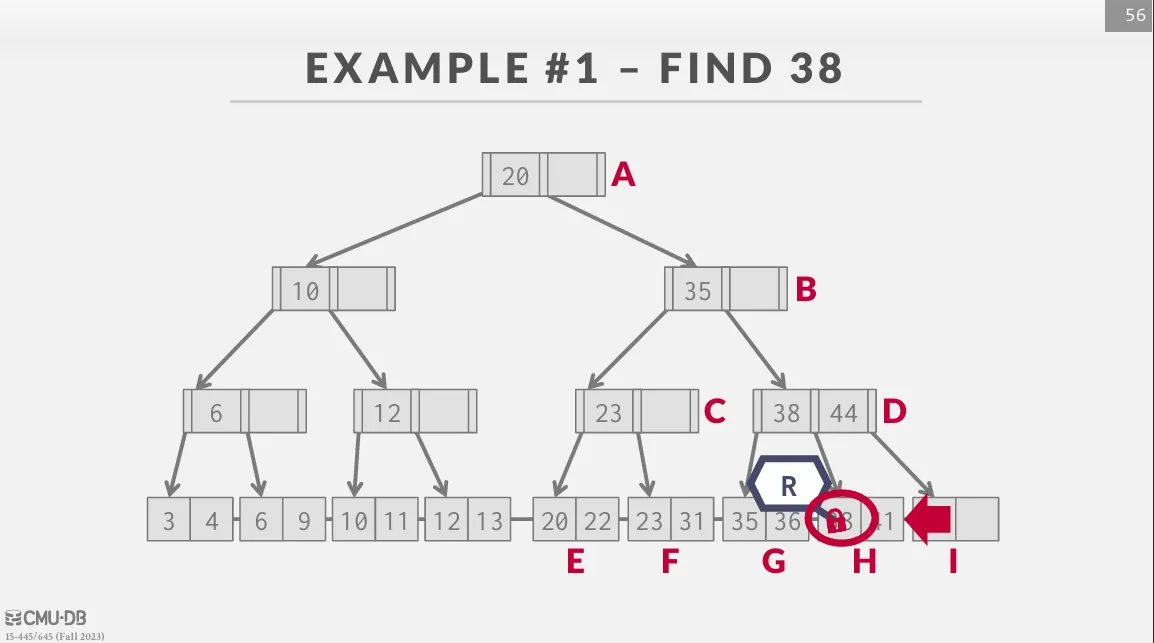
Search
從 root 開始往下遍歷,不斷的獲取 child 的 read latch 並釋放 parent 的 latch 直到 leaf node。
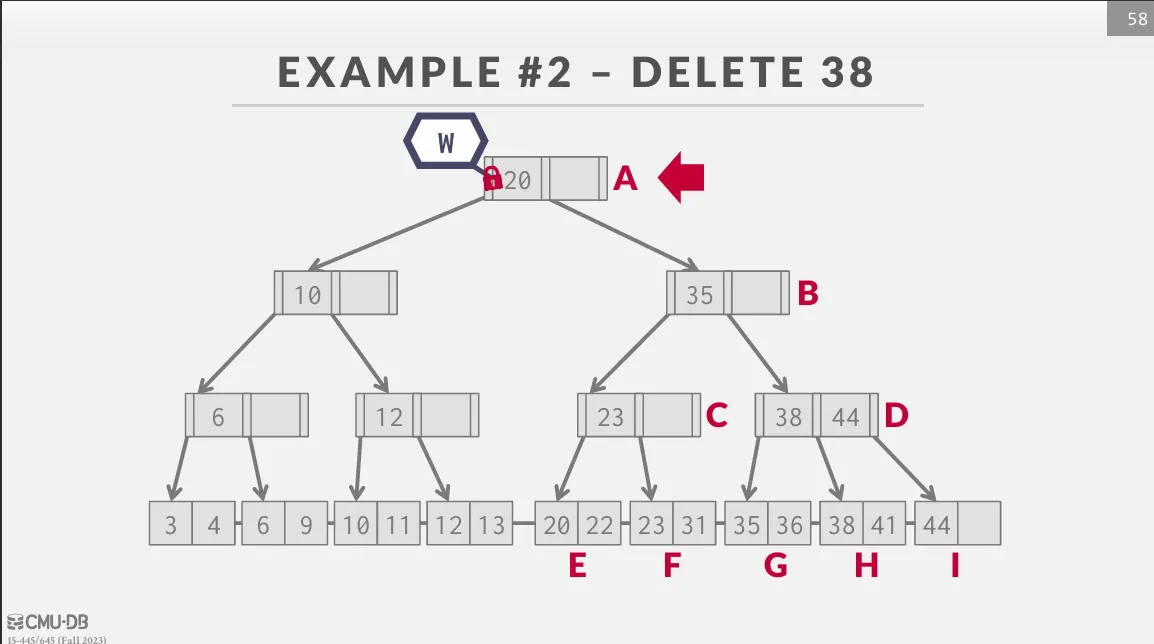
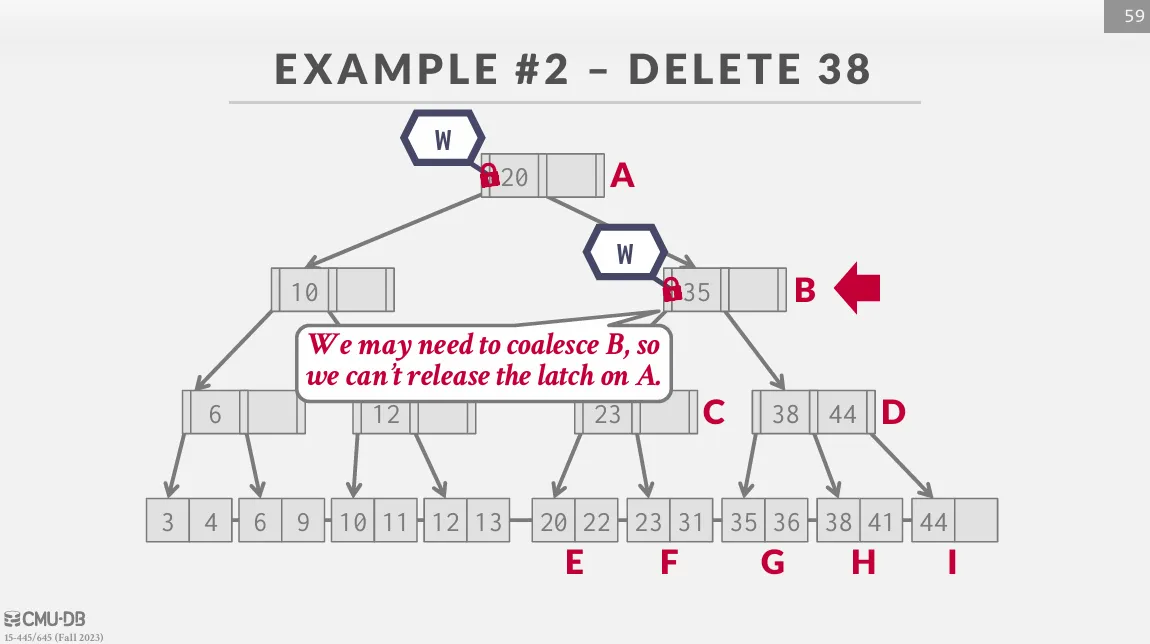
Insert / Delete
從 root 開始往下遍歷,並獲取 child 的 write latch,如果獲取就檢查 child 是否 safe,如果是的話就釋放之前獲取的所有 latch。
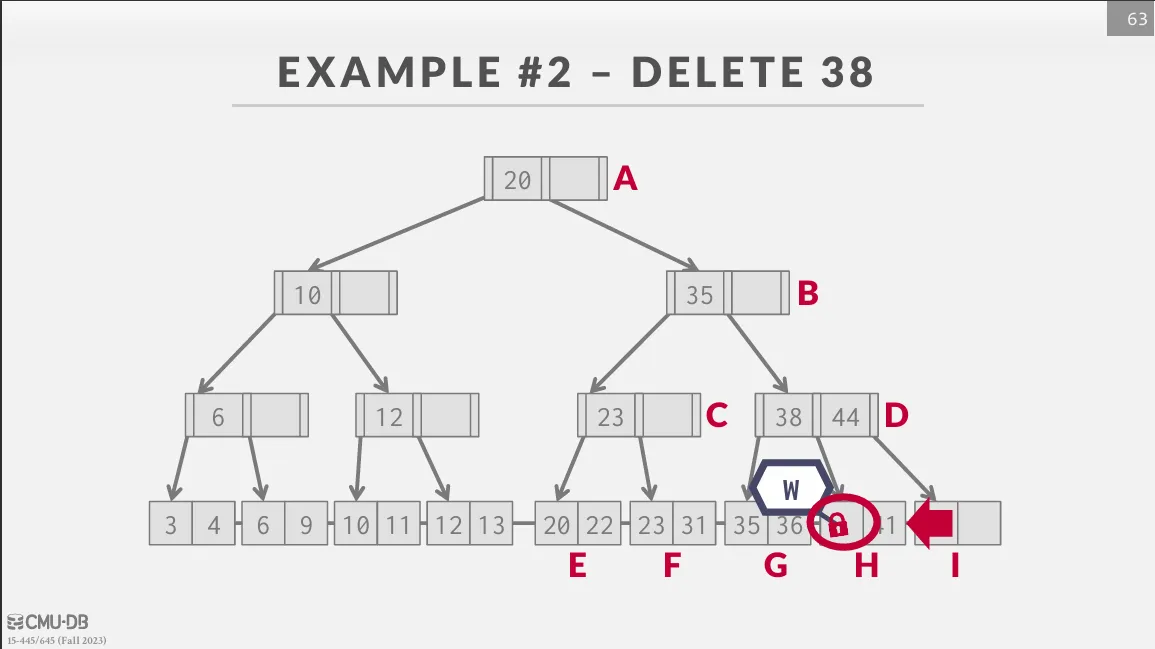
Better Latching Algorithm
在實際的應用中,每次都要在路徑中獲取 write latch 很容易成為瓶頸 (特別是 root node),並且大部分的操作並不會造成 merge / split,因此我們可以採用一種較為樂觀的方式。 在遍歷的時候使用 read latch,到達 leaf node 的時候再獲取 write latch 來更新或刪除值,如果在過程中發現有 merge / split 的情況,就重新從 root 開始直接原始的 latch crabbing。
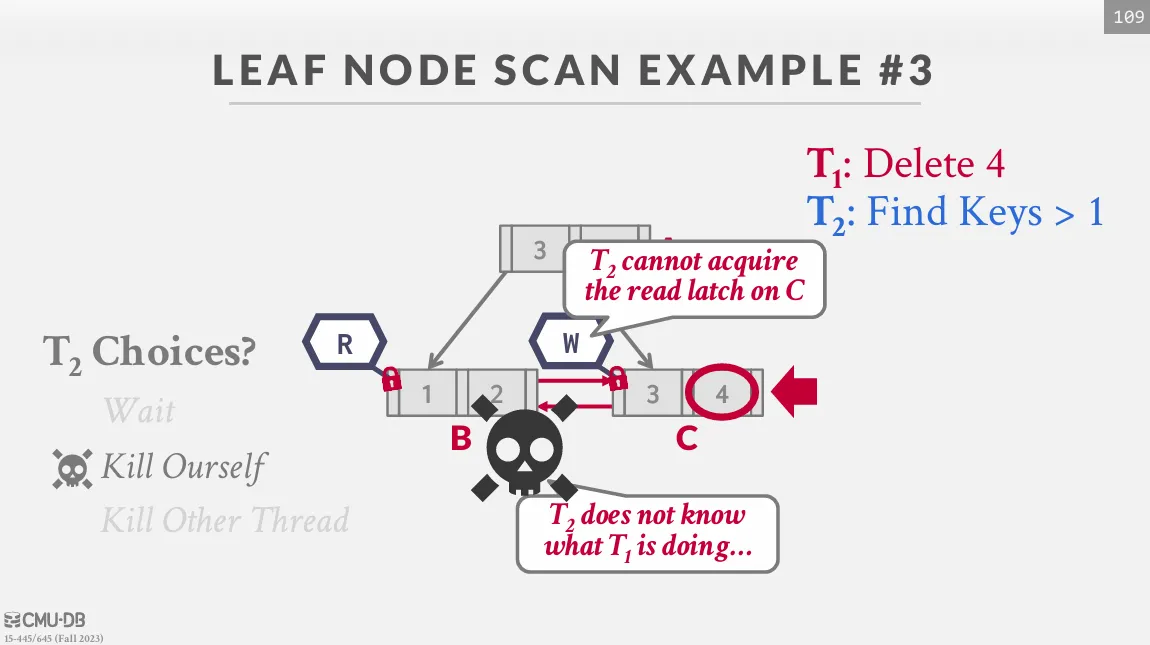
Leaf Node Scans
前面只有討論 top-down 的 latch crabbing,但在 range query 中,我們會需要進行橫向的訪問。
在 top-down 的訪問中, thread 只能從下層節點來獲取 latch,如果 latch 無法被獲取,thread 就需要等待,因此避免了 deadlock 的問題。 但在 leaf node scans 中,如果 thread 1 嘗試進行 scan,而 thread 2 則在刪除節點,就會導致 deadlock 的問題。
當獲取 latch 失敗時,thread 應該快速停止所有動作並且釋放所有 latch,最後再重新開始,這是因為我們需要盡量避免長時間的等待以及不需要的計算。