Indexes & Filters
Index 跟 Filter 是 DBMS 中非常重要的概念,能夠幫助我們更快地查找資料。
Index 用於快速查詢資料在表中的實際位置,像是 B+Tree Index、Hash Index。 Filter 則是用於快速判斷某個資料是否可能存在集合中,像是 Bloom Filter。
B-Tree
B-Tree Family
B-Tree 中的 B 通常代表 Balanced,而 B-Tree 的變種有很多,例如 :
- B-Tree
- B+Tree
- B* Tree
- Tree
其中最常見的是 B+Tree,各個 DBMS 也會使用不同的 B-Tree 家族的變種,如 PostgreSQL 使用了 Lehman and Yao's high-concurrency B-tree management algorithm。
B+Tree
B+Tree 是一種 self-balancing 的多路搜尋樹,能在 search、insert、delete 操作中保證 的時間複雜度,並且在 sequential access(如 range scan)時能有效率地達成 的複雜度,其中 為輸出資料量。
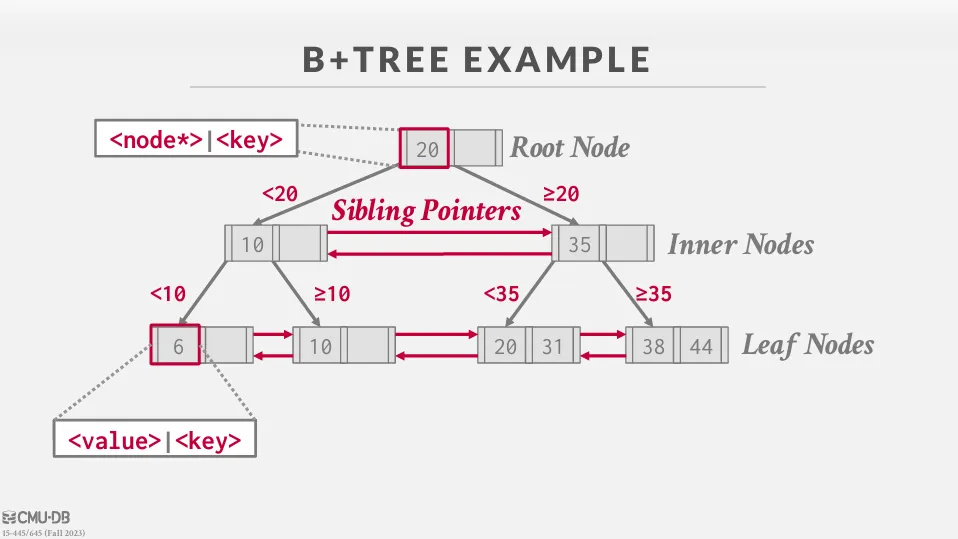
M-way B+Tree 的特點有 :
- 每個節點最多儲存 M 個 key,並且有 M+1 個 children
- 每個 leaf node 的深度都相同 (perfectly balanced)
- 除了 root node 以外,每個節點都至少要有 個 key (半滿)
- leaf node 會透過 doubly linked list 連接,提高 sequential access 的效率
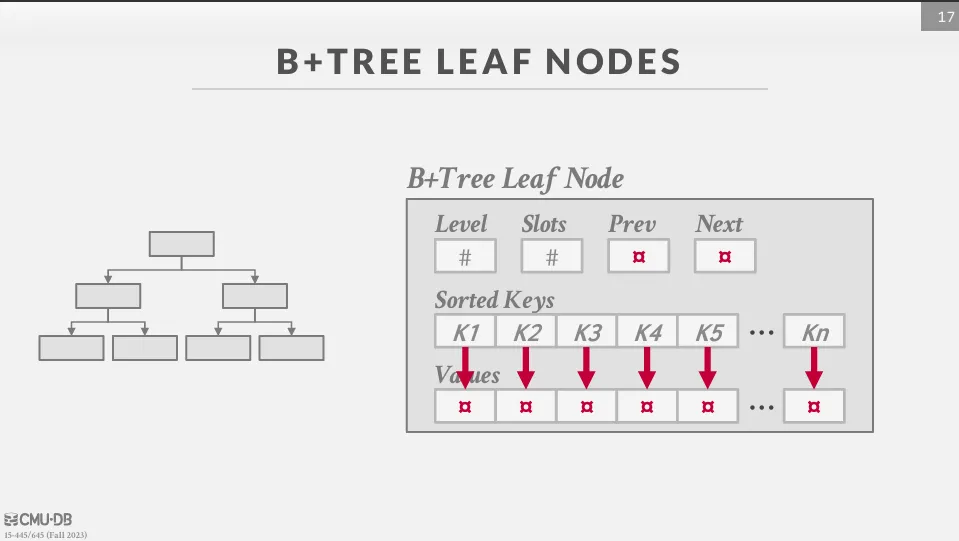
每個 node 中都包含了一個經過排序的 key / value 陣列,其中 key 就是 index 的值,而 value 則會根據是 inner node 或 leaf node 而有所不同。
其中 inner node 的值就是指向下一個節點的指標,而 leaf node 的值則有兩種不同的實作方式 :
- Record IDs : 直接儲存指向 tuple 的指標
- Tuple Data : 直接儲存 tuple 的資料,但對於 secondary index 來說,這樣會造成重複儲存
B+Tree Operations
有關 B+Tree 的操作,可以參考 這個網站。
我們也會在 Project #2 中實作 B+Tree 的各種操作。
B+Tree vs B-Tree
B-Tree 的資料分布在 internal 和 leaf node,而 B+Tree 所有資料都存在葉節點,internal node 只存 key,這導致 B+Tree 的高度通常更低,搜尋起來會更穩定。
除此之外,B+Tree 的葉節點有鏈結,所以在 sequential 或 range query 上效率遠高於 B-Tree。 雖然兩者的 search、insert、delete 複雜度都是 ,但因為 B+Tree 更適合硬碟存取,所以在實際應用中會比 B-Tree 更有效率。
Composite Indexes
B+Tree 可以支援 composite indexes,也就是可以在一個 index 中儲存多個 key。
CREATE INDEX idx ON table_name (key1, key2, key3);
這樣的 index 可以用來加速查詢,並且可以支援多個 key 的查詢,但必須遵守最左匹配規則 (leftmost indexing rule),也就是說,查詢時必須從左到右使用 index 中的 key。
-- ok
SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE key1 = 1 AND key2 = 2 AND key3 = 3;
-- ok
SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE key1 = 1 AND key2 = 2;
-- ok
SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE key1 = 1;
-- only key1 index is used
SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE key1 = 1 AND key3 = 3;
-- not ok
SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE key2 = 2 AND key3 = 3;
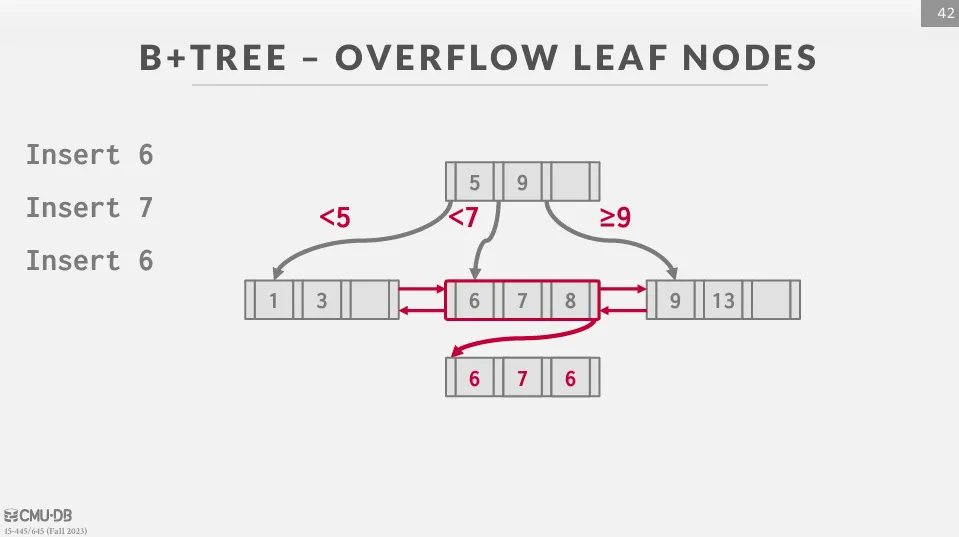
Duplicate Keys
有兩種常見的方式來處理 duplicate keys :
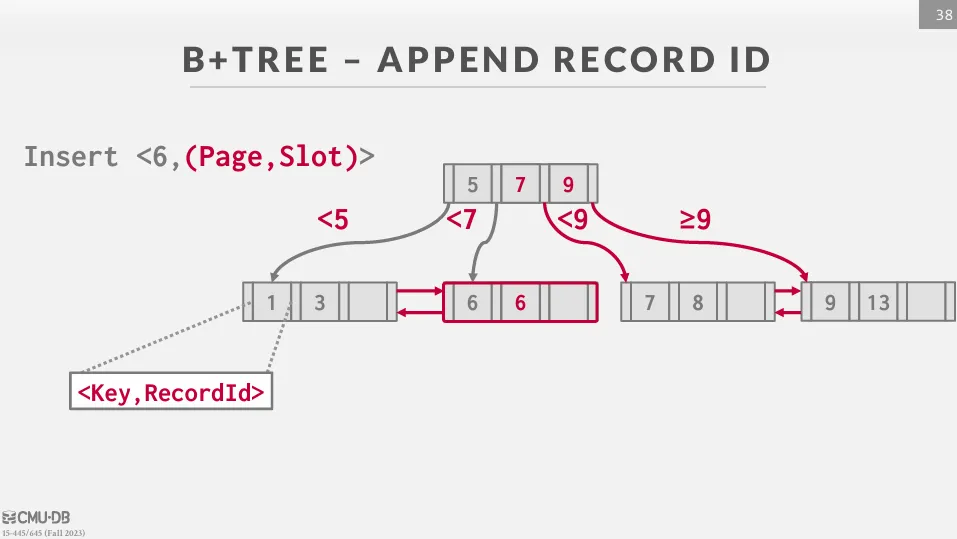
- Append Record ID : 把唯一的 Record ID 附加在 key 後面,這樣可以保證每個 key 都是唯一的,但會增加 index 的大小。
- Overflow Leaf Nodes : 允許節點溢出來儲存 duplicate keys。
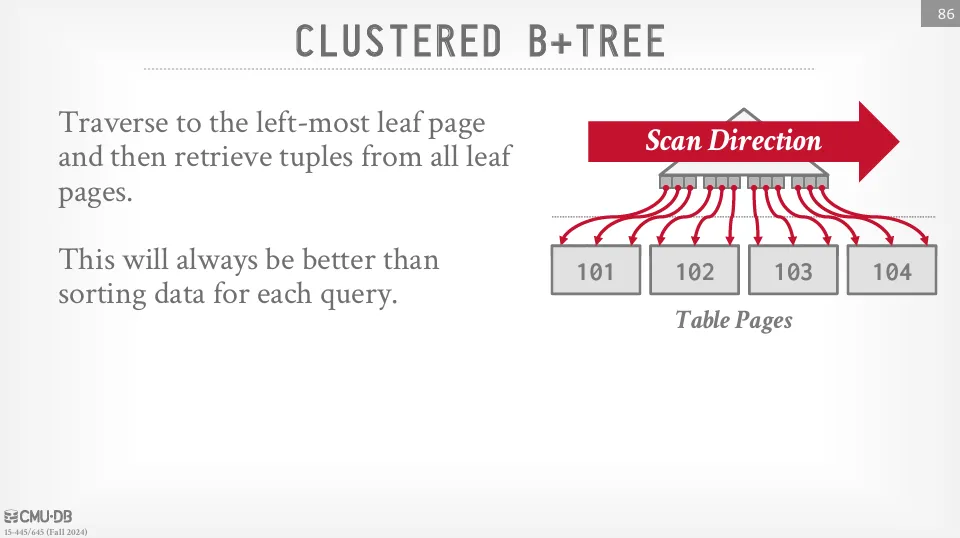
Clustered Indexes
Clustered Index 是一種資料實體的排序方式,會讓資料表的資料依照某個欄位排序儲存,而不是隨機或插入順序。 這對於範圍查詢非常有用,因為可以直接從硬碟上讀取連續的資料頁面。
在 PostgreSQL 中,我們可以使用以下的 SQL 指令來做一次 one-time 的 clustering :
CLUSTER table_name USING index_name;
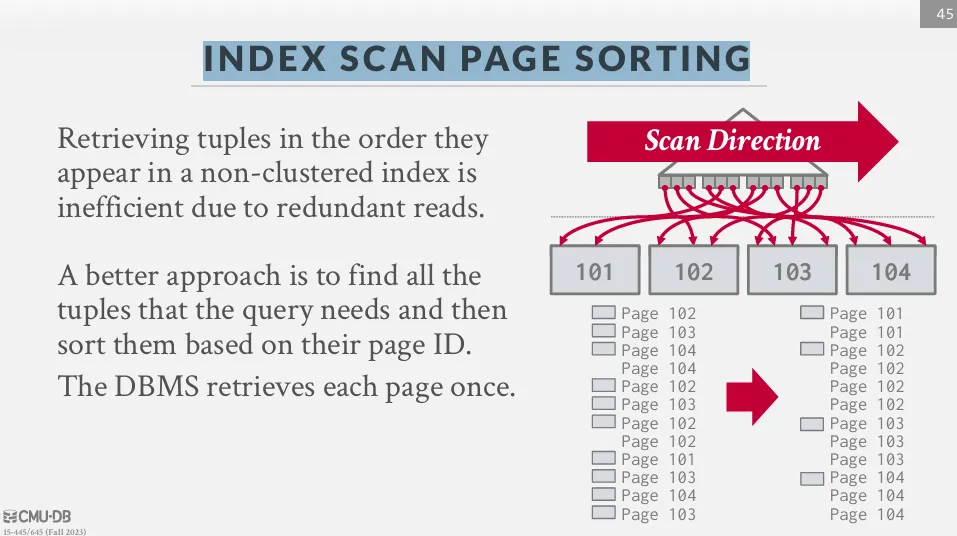
Index Scan Page Sorting
由於直接從 unclustered index 中取得資料非常沒效率,因此 DBMS 可以先把要用的 tuple 都找出來,然後根據 page_id 做排序,這樣就可以減少硬碟的隨機存取。
B+Tree Design Choices
B+Tree 看似是一個單純的資料結構,但實際上有很多設計上的選擇會影響它的效能。
Node Size
一般來說,硬碟 I/O 包含了 seek time 跟 transfer time,對於 HDD 來說,seek time 通常是主要的瓶頸,因此我們希望每次讀取的資料量越多越好,而對於 In-Memory 來說,cache miss 才是主要的瓶頸,因此我們希望每次讀取的資料量剛好能塞進 cache line。
也因此,不同的儲存媒介會有不同的最佳 node size :
- HDD : 1MB
- SSD : 10KB
- In-Memory : 512B
Merge Threshold
由於 B+Tree 的合併開銷很大,所以有些 DBMS 並不會在每次插入時都合併,而是會由其他的 process 來定期處理合併。
Variable Length Keys
處理不定長度的 key 有以下幾種方式 :
- Pointers : 儲存一個指標指向 tuple
- Variable-Length Nodes : 允許可變長度,但需要精細的記憶體管理
- Padding : 將 key 填滿到固定長度
- Key Map / Indirection : 使用一個固定長度的 key map 來指向實際的 key / value,有點類似 slotted page
如果一個 key 就比 node 還大,那就需要再把它存到 overflow page 中來處理。 在 PostgreSQL 中,這個 overflow page 被稱為 TOAST (The Oversized-Attribute Storage Technique),當有超過 2KB 的資料時,就會切成多塊並存到獨立的 TOAST 表中。
Intra-Node Search
在節點內搜索有三種方式 :
- Linear : 遍歷整個節點。線性掃描對 CPU cache 友善,並且能搭配 SIMD 指令來進行加速,因此即使 B+Tree 的節點內是排序過的,線性掃描仍然是常見的選擇。
- Binary : 二分搜索,演算法複雜度比較低,但對 CPU cache 不友善
- Interpolation : 用 key 的分布來估計位置,舉例來說,如果 key 是 1 到 1000 之間的數字,且我們要找 500,那就可以直接跳到中間的位置。
SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) 是一種平行運算的技術,可以讓 CPU 在同一個指令週期內對多個資料進行相同的操作,與之相對的是 SISD (Single Instruction, Single Data),也就是傳統的單一資料流處理方式。
在現代的 CPU 中,除了有 eax 這種通用的暫存器外,還有一種叫做向量暫存器 (vector register) 的東西,常見的有 XMM (128-bit)、YMM (256-bit)、ZMM (512-bit) 等等,這些向量暫存器可以一次儲存多個資料。
而 SIMD 指令集就是用來操作這些向量暫存器的,它可以讓我們在一個指令週期內對多個資料進行相同的運算,如 _mm_add_epi32 可以同時對向量暫存器中的四個 32-bit 整數進行加法運算,_mm_cmpgt_epi32 可以同時比較向量暫存器中的四個 32-bit 整數。
B+ Tree Optimizations
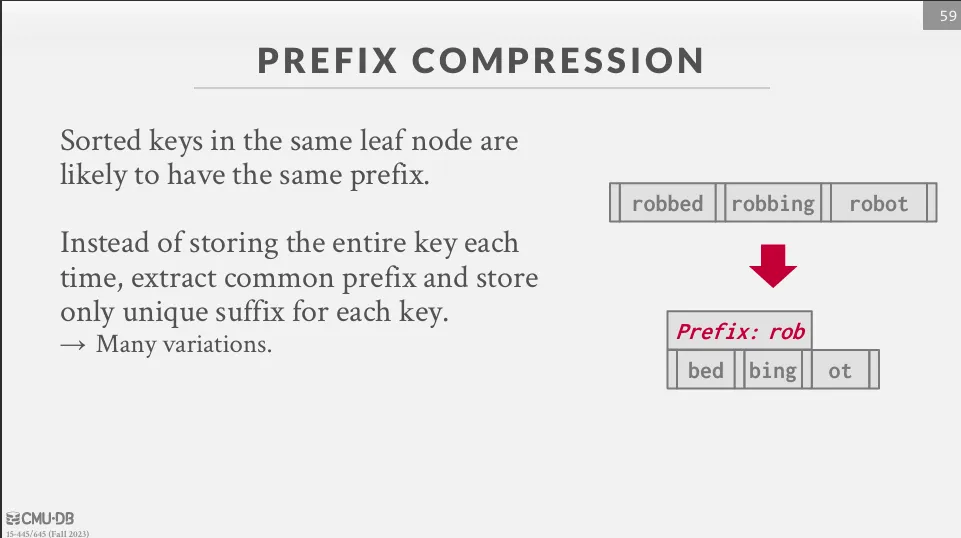
Prefix Compression
同一個 node 常常有相同的 key,我們可以透過 prefix 來減少儲存空間。
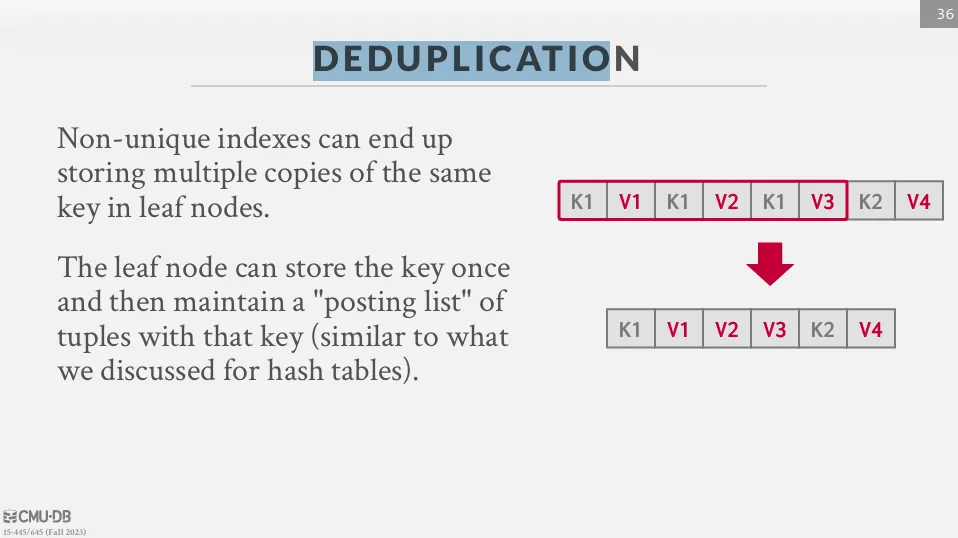
Deduplication
可以將重複的 key 合併。
Suffix Truncation
在 inner node 中, key 只是用來決定要往左還是往右走,因此只需要儲存可供辨識的部分。 例如 key 是 abcdefgh,我們可以只儲存 abc。
Pointer Swizzling
在 DBMS 中,如果我們要查詢一個 page 的位置,通常要帶著 page_id 來查詢 page table,但如果這個 page 已經固定在 buffer pool 中,我們就可以使用原始指標而不需要再訪問 page table。
Bulk Insert
最快建立 B+Tree 的方法是將 key 先排好序,再從下往上建立 B+Tree,適合在大量資料匯入時使用。
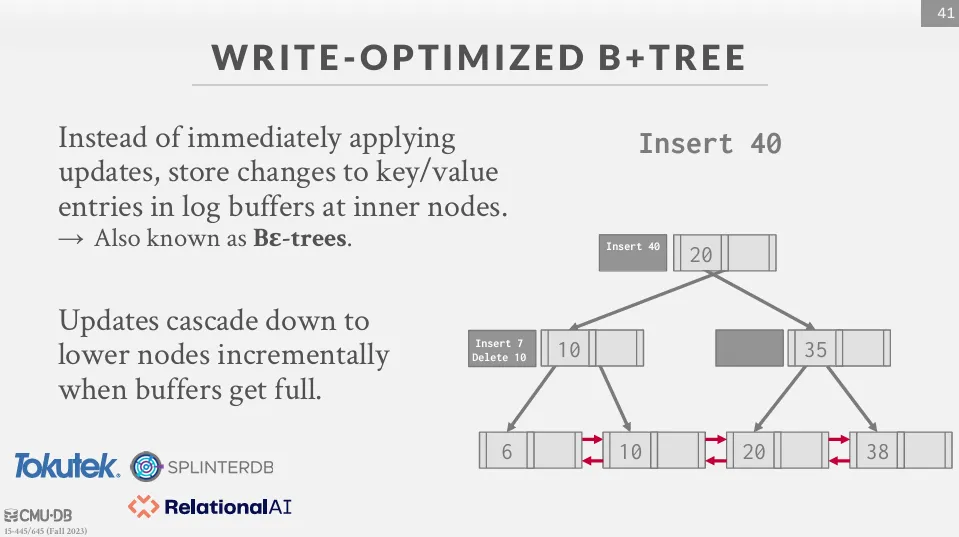
Write-Optimized B+ Tree
因為分裂和合併節點在 B+Tree 中非常耗時,因此有些 B-Tree 的變體會延遲這些行為,如 -Tree,這種樹會將變動儲存在 log 檔並慢慢往下傳遞。
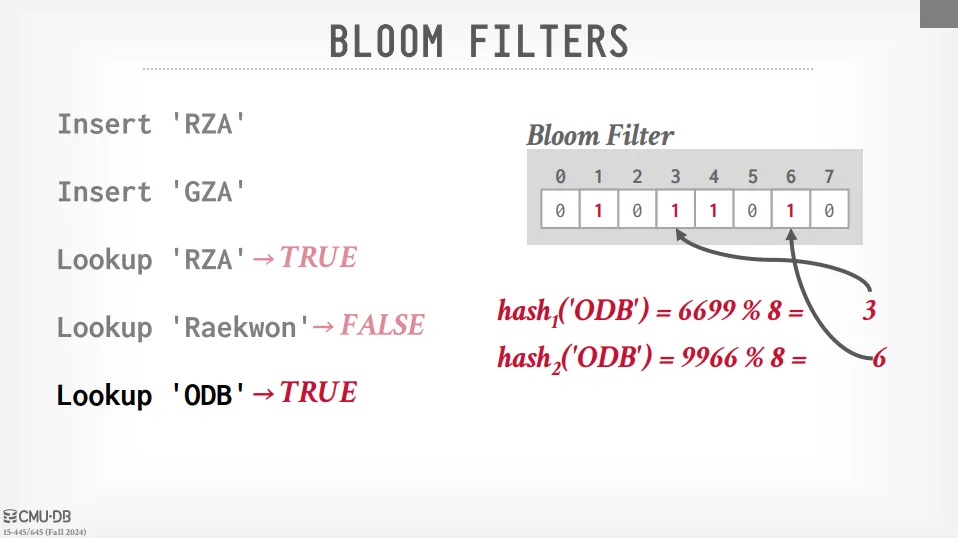
Bloom Filter
Bloom Filter 是一種機率型的資料結構,提供了 insert 跟 lookup 的功能 (沒有 delete),可以幫助我們快速的判斷某個資料是否存在於集合中。 有可能會產生 false positive (沒有這個資料,但回傳有),但不會產生 false negative (有這個資料,但回傳沒有)。
操作方法如下:
- 初始化一個位元陣列 (bitmap),大小為 m 位元。
- 選擇 k 個 hash function,這些 hash function 可以將資料映射到 0 到 m-1 的範圍內。
- 當插入一個資料時,使用 k 個 hash function 計算出 k 個位置,將這些位置的位元設為 1。
- 當查找一個資料時,使用 k 個 hash function,檢查 k 個位置是否都是 1,如果是,則可能存在,如果有任何一個位置是 0,則一定不存在。
除了比較正統的 Bloom Filter 之外,還有一些變體 :
- Counting Bloom Filter : 使用計數器來代替位元陣列,這樣可以支援刪除操作。
- Cuckoo Filter : 使用 cuckoo hashing 跟 fingerprint 技術來減少 false positive 的機率,並且支援刪除操作。
- Succinct Range Filter : 一種不可修改的 Bloom Filter,使用位元陣列來表示一個範圍內的值是否存在。
Skip List
Skip list 是一種基於 linked list 的資料結構,提供了類似於平衡樹的查找效率 ,但實現起來更簡單。 它使用多層 linked list 來跳過一些節點,從而加快查找速度。
與 B+Tree 一樣,Skip list 以有序的方式儲存資料,不同的是在插入跟刪除的時候,Skip list 不需要進行分裂或合併節點,而是透過隨機選擇 (丟硬幣) 的方式來維持平衡。
Skip list 提供了三種操作,分別是插入、刪除和查找。
- 查找:從最高層開始,只要下一個節點小於目標值就繼續往右走,不然的話就往下一層走,直到到達最底層為止。
- 插入:
- 首先需要隨機選擇一個層級,從最低即開始丟硬幣決定是否要在這一層插入,如果不是的話就向上移動一層直到最高層為止,確保每層的分布是對數級別的。
- 然後跟查找一樣,從最高層開始,找到每一層中正確的插入位置。
- 最後從最底層開始插入節點,直到目標層級。從下到上插入的原因是為了併發性,因為只有最底層的被連接好之後,這個節點才算是對外可見的,搭配 CAS 甚至可以做到無鎖的插入。
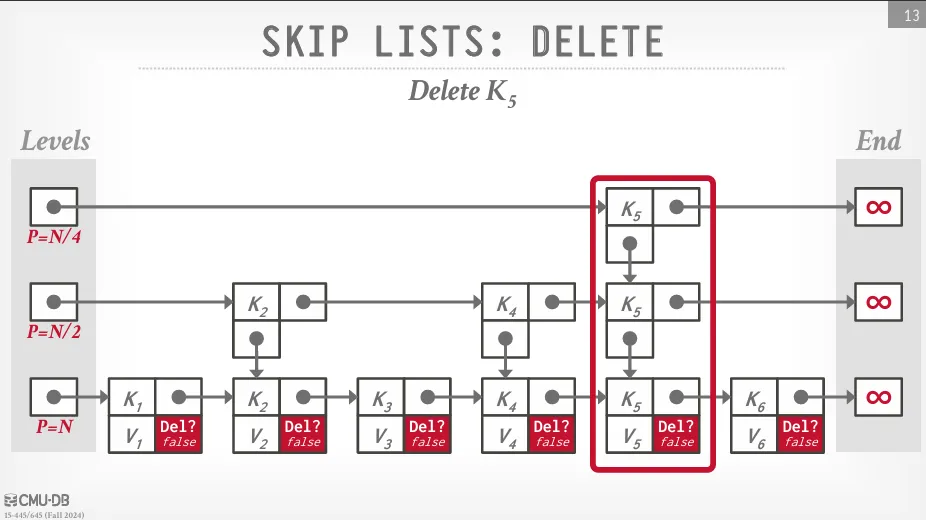
- 刪除:
- 先找出所有要刪除的節點,接著做軟刪除,最後 GC 會定期清理這些軟刪除的節點。
Skip list 的主要優點在於不需要做 rebalancing,這也就代表了鎖的開銷會相對較低,且如果不使用 reverse pointer 的話記憶體的用量也會相對較少。 缺點在於不利於硬碟快取,因為有不同層級的節點會分布在不同的記憶體位置,這樣會導致 cache miss 的機率增加,且如果沒有 reverse pointer 的話反向搜索會相對困難。
Trie
因為 B+Tree 不提供關於內部節點下方是否存在節點的資訊,所以要判斷一個鍵是否存在就必須遍歷到葉節點,這可能導致多次昂貴的磁碟 I/O (cache miss)。
字典樹是一種樹形的資料結構,它將鍵儲存為數字 (或字元),並且每個節點代表一個數字的前綴。 這些數字可以是 ASCII 字元、Unicode 字元或其他類型的數字。 字典樹的每個節點都包含一個指向下一層節點的指針,這些指針可以用來快速地查找鍵是否存在,且複雜度與鍵的長度成正比。
跨度 (span) 是指一個數字所佔用的位元數,如果是二進位的話,則跨度為 2。 如果這個數字及其前綴存在於資料集合中,那麼在該數字處會儲存一個指向下一層節點的指針,否則就儲存 null。
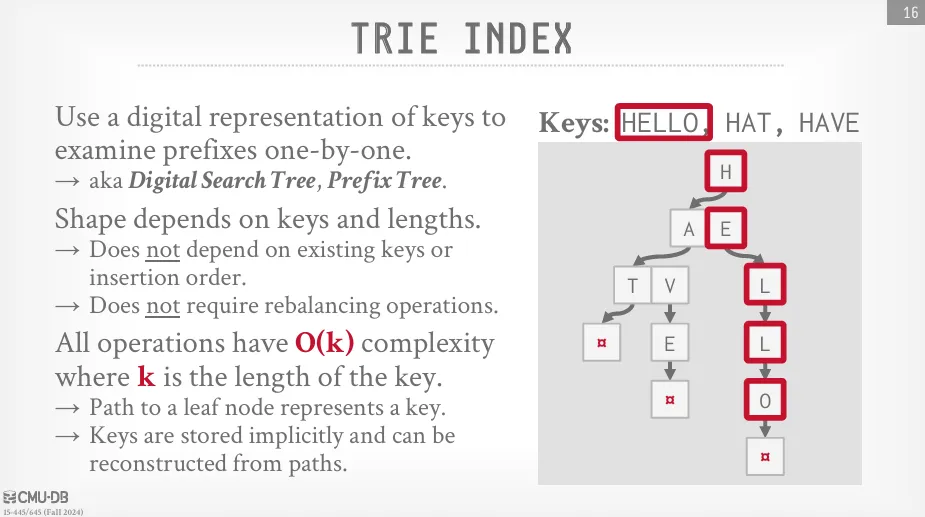
在實際應用中,Trie 的節點可能會非常稀疏,或是單一的分支過於冗長,因此我們可以採用壓縮的方式來儲存 :
- 水平壓縮 (Horizontal Compression) : 如果同一層級的 span 很大且很空,可以考慮改成使用 array 來儲存
- 垂直壓縮 (Vertical Compression) / 基數樹 (Radix Tree) : 如果只有一個單一的分支,可以考慮將這個分支直接合併到父節點中,這樣可以減少節點的數量,但這樣有可能造成錯誤,因此最後還是需要跟原本的 tuple 做比對。
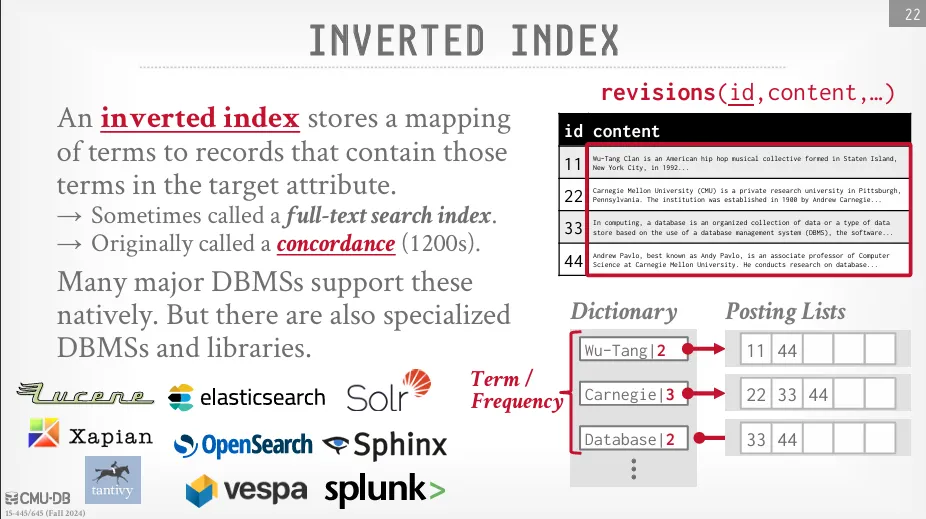
Inverted Index
前面討論的資料結構主要適用於查找一個確切的值,它們不支援關鍵字搜尋。 舉例來說,如果我們想查詢所有包含 Taiwan 這個詞的維基百科文章,傳統索引就無法直接做到,這就是為什麼需要 Inverted Index 的原因。
倒排索引儲存的是詞 (terms) 到包含這些詞項的記錄 (records) 之間的映射。 這些包含詞的記錄列表被稱為 posting list,簡單來說,它就像一本書的索引,但不是按照頁碼順序排列詞語,而是按照關鍵字來查找包含該詞語的所有文檔或記錄。
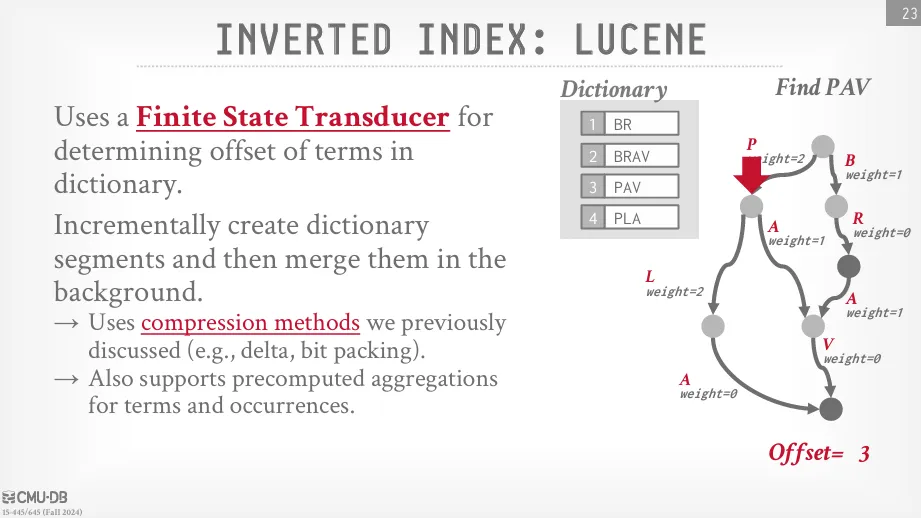
Lucene
Lucene 是一個專門的倒排索引引擎,它儲存倒排索引的方式是使用一種類似於字典樹的資料結構,稱為有限狀態轉換器 (finite state transducer, FST)。 與字典樹直接儲存指向元組的指針不同,有限狀態轉換器在每條邊上儲存權重,當你沿著路徑遍歷到你正在尋找的鍵時,這些權重的滾動加總最終會給你這個詞項在映射中儲存的確切位置。 這使得 Lucene 能夠高效地從詞項映射到其 posting list。
在 Lucene 的詞項字典中 (這是儲存所有唯一詞項的部分),由於它是不可變的且預先構建的,因此可以應用多種壓縮技術,例如 :
- 差分壓縮 (delta compression): 儲存相鄰值之間的差異,而不是每個值的完整形式,從而減少儲存空間。
- 位元打包 (bit-packing): 根據實際數據的位元需求來儲存數據,而不是使用固定的字節數,這在數值範圍不大時能顯著節省空間。
此外,Lucene 還支援預聚合 (pre-aggregation),這可以加速基於詞項分組的聚合查詢。
PostgreSQL
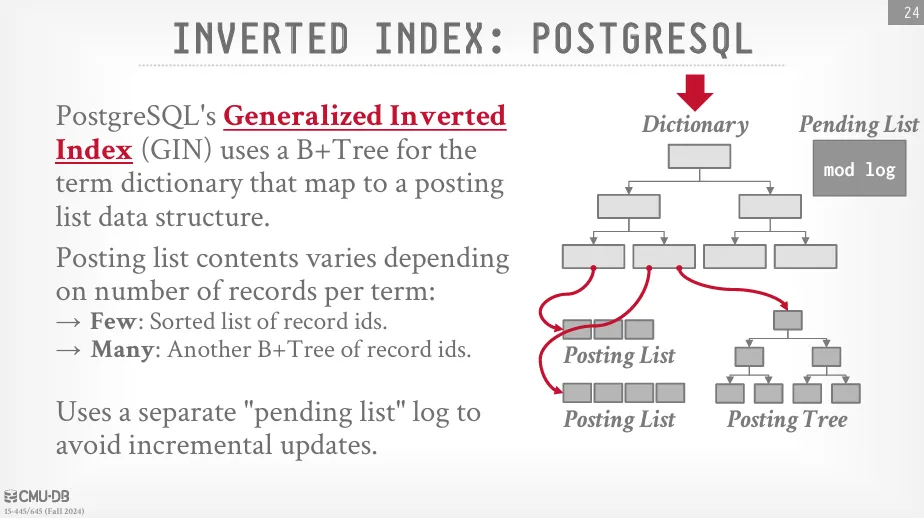
PostgreSQL 的通用倒排索引 (Generalized Inverted Index, GIN) 使用 B+Tree 來構建字典。這個 B+Tree 葉節點的值 (即發布列表的儲存方式) 取決於發布列表的大小 :
- 對於較小的 posting list,葉節點中直接儲存的是一個排序過的記錄 ID 列表。
- 對於較大的 posting list,PostgreSQL 會為這些發布列表額外構建獨立的 B+Tree 來儲存記錄 ID,以提高訪問效率。
PostgreSQL 還使用一個單獨的 pending list 來避免頻繁的小規模增量更新。 當有新的更新時,它們會先被記錄在這個待處理列表中,然後累積起來,最終以批次插入的方式一次性應用到主字典中。
Vector Index
倒排索引雖然支援關鍵字搜尋,但它無法理解內容的語義意義,這代表要找到的關鍵字必須完整地包含在內容中。 舉例來說,如果一個應用程式想要搜尋與特定主題相關的記錄,比如 "關於俚語的嘻哈團體歌曲",在這種情況下,我們就需要一種除了倒排索引之外的其他方法。 倒排索引只能找到包含 "俚語"、"嘻哈"、"團體"、"歌曲" 等詞的文檔,但它無法理解這些詞組合起來的整體概念或語義上的相關性。
LLM 以其能夠為文本生成 embedding 而聞名,這些嵌入本質上是浮點數的陣列。 如果兩個文本在語義上相似,它們的嵌入在幾何空間中也會彼此接近。 因此,專門用於最近鄰搜尋 (nearest-neighbor search, NN) 的向量索引就能夠幫助我們解決上述類型的查詢。
然而,與我們之前看到的傳統查詢不同,這種基於語義相似性的查詢沒有一個絕對正確的答案,結果往往是相關度最高的幾個選項。 此外,在找到最近鄰居之前或之後,通常還需要對數據進行額外的過濾 (例如分類等等),以滿足更精確的業務需求。
Inverted File
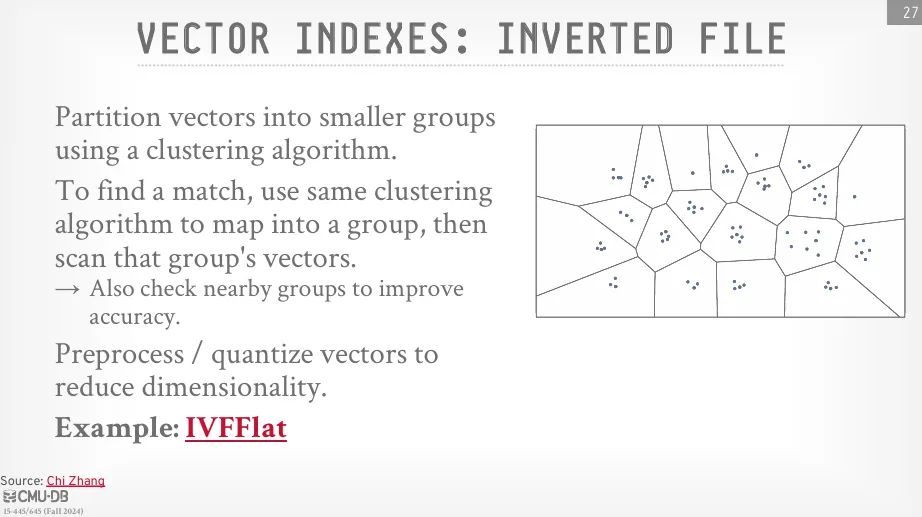
倒排檔案方法透過聚類演算法 (clustering algorithm) 將高維向量劃分成較小的群組。 當進行最近鄰搜尋時,會使用相同的聚類演算法將查詢向量定位到一個或幾個相關的群組中。 然後,只在這些被定位到的群組內部查找所有向量,以找到最近的鄰居 (有時也需要檢查附近的群組,以防最佳鄰居位於群組邊界)。 一個典型的例子是 IVFFlat 演算法。
為了進一步提升查找速度,可以對索引執行預處理 (preprocessing) 和量化 (quantization)。這些技術可以降維或降低其精度,從而加快查找時間。
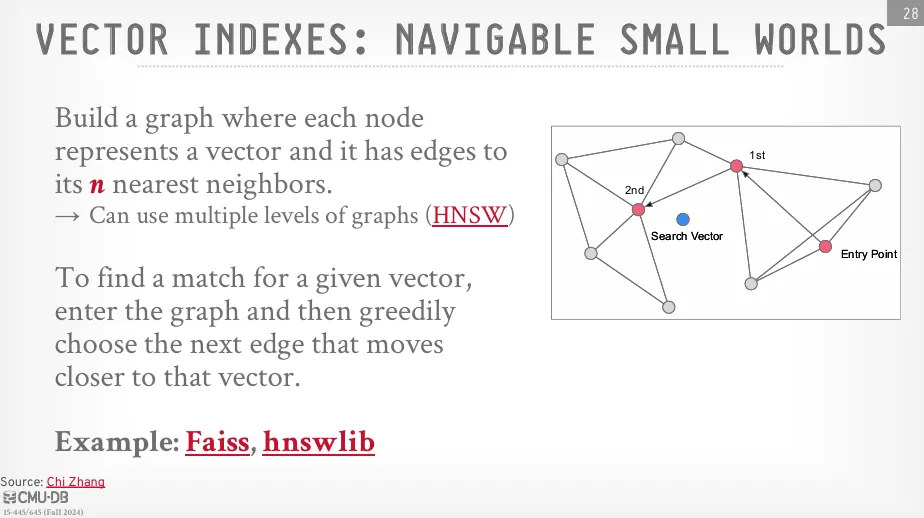
Navigable Small Worlds
Navigable Small Worlds 是一種基於圖的近似最近鄰搜尋方法。 它構建一個表示向量之間鄰居關係的圖,圖中的每個節點 (node) 代表一個向量,而它的邊 (edges) 則連結到其 n 個最近的鄰居。
當進行最近鄰搜尋時,Navigable Small Worlds 利用這個圖,從一個定義好的入口點開始,透過 greedy algorithm 選擇那些能讓它更接近查詢向量的邊,來逐步導航。 兩個知名的實現例子是 FAISS 和 HNSWlib (Hierarchical Navigable Small Worlds)。